Cervical cancer prevention and care in HIV clinics across sub-Saharan Africa: results of a facility-based survey
- PMID: 38979918
- PMCID: PMC11232047
- DOI: 10.1002/jia2.26303
Cervical cancer prevention and care in HIV clinics across sub-Saharan Africa: results of a facility-based survey
Abstract
Introduction: To eliminate cervical cancer (CC), access to and quality of prevention and care services must be monitored, particularly for women living with HIV (WLHIV). We assessed implementation practices in HIV clinics across sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) to identify gaps in the care cascade and used aggregated patient data to populate cascades for WLHIV attending HIV clinics.
Methods: Our facility-based survey was administered between November 2020 and July 2021 in 30 HIV clinics across SSA that participate in the International epidemiology Databases to Evaluate AIDS (IeDEA) consortium. We performed a qualitative site-level assessment of CC prevention and care services and analysed data from routine care of WLHIV in SSA.
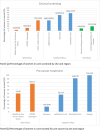
Results: Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination was offered in 33% of sites. Referral for CC diagnosis (42%) and treatment (70%) was common, but not free at about 50% of sites. Most sites had electronic health information systems (90%), but data to inform indicators to monitor global targets for CC elimination in WLHIV were not routinely collected in these sites. Data were collected routinely in only 36% of sites that offered HPV vaccination, 33% of sites that offered cervical screening and 20% of sites that offered pre-cancer and CC treatment.
Conclusions: Though CC prevention and care services have long been available in some HIV clinics across SSA, patient and programme monitoring need to be improved. Countries should consider leveraging their existing health information systems and use monitoring tools provided by the World Health Organization to improve CC prevention programmes and access, and to track their progress towards the goal of eliminating CC.
Keywords: HIV; cervical cancer prevention; monitoring; outcomes; prevention and care cascades; sub‐Saharan Africa.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of the International AIDS Society published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International AIDS Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global strategy to accelerate the elimination of cervical cancer as a public health problem. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
-
- WHO guideline for screening and treatment of cervical pre‐cancer lesions for cervical cancer prevention, second edition. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Comprehensive cervical cancer control: a guide to essential practice–2nd ed. 2014. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Monitoring national cervical cancer prevention and control programmes: quality control and quality assurance for visual inspection with acetic acid (VIA)‐based programmes. 2013.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI096299/Central Africa
- AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI124872/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069911/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- U01 AI069919/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI069924/Southern Africa
- U01AI069919/West Africa
- R24AI24872/Harmonist project
- U54 AG062334/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI096299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 801076/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant)
- U54 CA190163/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI069911/East Africa
- 177319/Swiss National Science Foundation (r4d program)
- DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
- DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U.S. National Institutes of Health's National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- U01 AI069924/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

