Synthesis, cytotoxicity, anti-inflammatory, anti-metastatic and anti-oxidant activities of novel chalcones incorporating 2-phenoxy-N-arylacetamide and thiophene moieties: induction of apoptosis in MCF7 and HEP2 cells
- PMID: 38980411
- PMCID: PMC11582173
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-024-03255-9
Synthesis, cytotoxicity, anti-inflammatory, anti-metastatic and anti-oxidant activities of novel chalcones incorporating 2-phenoxy-N-arylacetamide and thiophene moieties: induction of apoptosis in MCF7 and HEP2 cells
Abstract
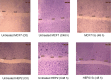
Eight Novel chalcones were synthesized and their structures were confirmed by different spectral tools. All the prepared compounds were subjected to SRB cytotoxic screening against several cancer cell lines. Compound 5c exerted the most promising effect against MCF7 and HEP2 cells with IC50 values of 9.5 and 12 µg/mL, respectively. Real-time PCR demonstrated the inhibitory effect of compound 5c on the expression level of Antigen kiel 67 (KI-67), Survivin, Interleukin-1beta (IL-1B), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and Protein kinase B (AKT1) genes. Flow-cytometric analysis of the cell cycle indicated that compound 5c stopped the cell cycle at the G0/G1 and G2/M phases in MCF7 and HEP2 treated cells, respectively. ELISA assay showed that Caspase 8, Caspase 9, P53, BAX, and Glutathione (GSH) were extremely activated and Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2), Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), BCL2, Malondialdehyde (MDA), and IL-6 were deactivated in 5c treated MCF7 and HEP2 cells. Wound healing revealed that chalcone 5c reduced the ability to close the scrape wound and decreased the number of migrating MCF7 and HEP2 cells compared to the untreated cells after 48 h. Theoretical molecular modeling against P53 cancer mutant Y220C and Bcl2 showed binding energies of -22.8 and -24.2 Kcal/mole, respectively, which confirmed our ELISA results.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Anti-oxidant; Chalcones; Intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis; Wound healing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: Not applicable. Consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Abdelwahab RE, Darweesh AF, Ragheb MA, Abdelhamid IA, Elwahy AHM (2023) Synthesis of New 2-(4-(1,4-Dihydropyridin-4-yl)Phenoxy)- N -Arylacetamides and Their Heterocyclic-Fused Derivatives via Hantzsch-Like Reaction. Polycycl Aromat Compd 43:1974–1986. 10.1080/10406638.2022.2039240
-
- Abdelwahab RE, Ragheb MA, Elwahy AHM, Abdelhamid IA, Abdelmoniem AM (2024) Conjugate and regiochemical addition of aminoazoles to 2-(4-(2,2-dicyanovinyl)phenoxy)-N-arylacetamide affording fused pyrimidines linked to phenoxy-N-arylacetamide: antibacterial activity, molecular docking, and DNA binding studies. J Mol Struct 1307:137946. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.137946
-
- Abdullah AH, Ibrahim NS, Algethami FK, Elwahy AHM, Abdelhamid IA, Salem ME (2024) Synthesis, molecular docking, and antimicrobial activity of novel scaffolds based on bis(thiazole) linked to 2-phenoxy-N-arylacetamide as new hybrid molecules. J Mol Struct 1302:137506. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.137506
-
- Abdullah AH (2023) Ph.D. thesis, Cairo University, Faculty of Science, Department of Chemistry: Synthesis of bis(functional) compounds
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

