Krüppel-like factor 2 is an endoprotective transcription factor in diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 38981608
- PMCID: PMC11901337
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00222.2024
Krüppel-like factor 2 is an endoprotective transcription factor in diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
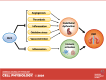
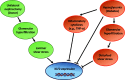
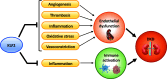
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a microvascular complication of diabetes, and glomerular endothelial cell (GEC) dysfunction is a key driver of DKD pathogenesis. Krüppel-like factor 2 (KLF2), a shear stress-induced transcription factor, is among the highly regulated genes in early DKD. In the kidney, KLF2 expression is mostly restricted to endothelial cells, but its expression is also found in immune cell subsets. KLF2 expression is upregulated in response to increased shear stress by the activation of mechanosensory receptors but suppressed by inflammatory cytokines, both of which characterize the early diabetic kidney milieu. KLF2 expression is reduced in progressive DKD and hypertensive nephropathy in humans and mice, likely due to high glucose and inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α. However, KLF2 expression is increased in glomerular hyperfiltration-induced shear stress without metabolic dysregulation, such as in settings of unilateral nephrectomy. Lower KLF2 expression is associated with CKD progression in patients with unilateral nephrectomy, consistent with its endoprotective role. KLF2 confers endoprotection by inhibition of inflammation, thrombotic activation, and angiogenesis, and thus KLF2 is considered a protective factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Based on similar mechanisms, KLF2 also exhibits renoprotection, and its reduced expression in endothelial cells worsens glomerular injury and albuminuria in settings of diabetes or unilateral nephrectomy. Thus KLF2 confers endoprotective effects in both CVD and DKD, and its activators could potentially be developed as a novel class of drugs for cardiorenal protection in diabetic patients.
Keywords: KLF2; eNOS; endothelial cells; glomerular hyperfiltration; shear stress.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LRG1 loss effectively restrains glomerular TGF-β signaling to attenuate diabetic kidney disease.Mol Ther. 2024 Sep 4;32(9):3177-3193. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.06.027. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38910328
-
Endothelial CXCR2 deficiency attenuates renal inflammation and glycocalyx shedding through NF-κB signaling in diabetic kidney disease.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Mar 25;22(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01565-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38528533 Free PMC article.
-
miR-214 and Its Primary Transcript Dnm3os Regulate Fibrosis and Inflammation Through RAGE Signaling in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Diabetes. 2025 Jul 1;74(7):1205-1219. doi: 10.2337/db24-0121. Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40183805
-
Vitamin B and its derivatives for diabetic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 12;1(1):CD009403. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009403.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25579852 Free PMC article.
-
Multidisciplinary management of diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Jul;14(7):169-207. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003011. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532796
Cited by
-
KLF2 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells by Regulating Nrf2 Expression.Int Dent J. 2025 Jun;75(3):1554-1563. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2025.02.019. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 40121852 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of the Primary Visual Cortex in Mice With Optic Nerve Injury.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 May 1;66(5):31. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.5.31. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40408096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weil EJ, Lemley KV, Mason CC, Yee B, Jones LI, Blouch K, Lovato T, Richardson M, Myers BD, Nelson RG. Podocyte detachment and reduced glomerular capillary endothelial fenestration promote kidney disease in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 82: 1010–1017, 2012. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.234. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK129467/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000345/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 DK109683/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK129467/HHS | NIH | NIDDK | Division of Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolic Diseases (DEM)
- R01 DK133912/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK122980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK117913/HHS | NIH | NIDDK | Division of Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolic Diseases (DEM)
- R01DK122980/HHS | NIH | NIDDK | Division of Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolic Diseases (DEM)
- P01 DK056492/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK109683/HHS | NIH | NIDDK | Division of Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolic Diseases (DEM)
- R01 DK117913/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

