Administration of an antibody against apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage prevents aortic aneurysm progression in mice
- PMID: 38982113
- PMCID: PMC11233551
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66791-7
Administration of an antibody against apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage prevents aortic aneurysm progression in mice
Abstract
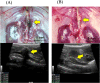
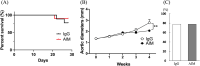
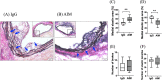
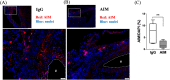
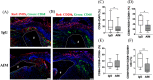
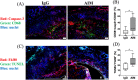
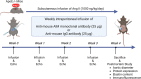
Apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage (AIM) is known to induce apoptosis resistance in macrophages and to exacerbate chronic inflammation, leading to arteriosclerosis. The role of AIM in aortic aneurysm (AA) remains unknown. This study examined the effects of an anti-AIM antibody in preventing AA formation and progression. In apolipoprotein E-deficient mice, AA was induced by subcutaneous angiotensin II infusion. Mice were randomly divided into two groups: (i) AIM group; weekly anti-murine AIM monoclonal antibody injection (n = 10), and (ii) IgG group; anti-murine IgG antibody injection as control (n = 14). The AIM group, compared with the IgG group, exhibited reduced AA enlargement (aortic diameter at 4 weeks: 2.1 vs. 2.7 mm, respectively, p = 0.012); decreased loss of elastic lamellae construction; reduced expression levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and MCP-1; decreased numbers of AIM-positive cells and inflammatory M1 macrophages (AIM: 1.4 vs. 8.0%, respectively, p = 0.004; M1 macrophages: 24.5 vs. 55.7%, respectively, p = 0.017); and higher expression of caspase-3 in the aortic wall (22.8 vs. 10.5%, respectively, p = 0.019). Our results suggest that administration of an anti-AIM antibody mitigated AA progression by alleviating inflammation and promoting M1 macrophage apoptosis.
Keywords: Aortic aneurysm; Apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage; Inflammation; Macrophage.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

