BRD4 plays an antiaging role in the senescence of renal tubular epithelial cells
- PMID: 38983468
- PMCID: PMC11228682
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-24-214
BRD4 plays an antiaging role in the senescence of renal tubular epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: Age-related kidney failure is often induced by a decrease in the bioavailability of tubular epithelial cells in elderly chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. BRD4, an epigenetic regulator and a member of the bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) protein family, acts as a super-enhancer (SE) organizing and regulating genes expression during embryogenesis and cancer development. But the physiological function of BRD4 in normal cells has been less studied. This study aimed to research certain biological roles of BRD4 in the process of normal cell aging and discuss the potential mechanisms.
Methods: In this study, we investigated the biological functions of BRD4 proteins in the aging of renal tubular cells. At first, we used a D-galactose (D-gal) and BRD4 inhibitor (Abbv-075) to replicate kidney senescence in vivo. D-gal and Abbv-075 were then used to measure the aging-related changes, such as changes in cell cycle, β-galactosidase activity, cell migration, and p16 protein expression in vitro. At last, we knocked down and over-expressed BRD4 to investigate the aging-related physiological phenomena in renal tubular cells.
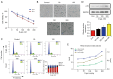
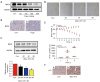
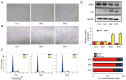
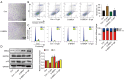
Results: In vitro, D-gal treatment induced noticeable aging-related changes such as inducing cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, increasing β-galactosidase activity as well as up-regulating p16 protein expression in primary human tubular epithelial cells. In the aging mice model, D-gal significantly induced renal function impairment and attenuated BRD4 protein expression. At the same time, the BRD4 inhibitor (Abbv-075) was able to mimic D-gal-induced cell senescence. In vivo, Abbv-075 also decreased kidney function and up-regulated p21 protein expression. When we knocked down the expression of BRD4, the senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) activity increased dramatically, cell migration was inhibited, and the proportion of cells in the G0/G1 phase increased. Additionally, the knockdown also promoted the expression of the senescence-related proteins p16. When the renal tubular cells were overexpressed with BRD4, cell aging-related indicators were reversed in the D-gal-induced cell aging model.
Conclusions: BRD4 appears to have an active role in the aging of renal tubular cells in vivo and in vitro. The findings also suggest that BRD4 inhibitors have potential nephrotoxic effects for oncology treatment. BRD4 may be a potential therapeutic biomarker and drug target for aging-related kidney diseases, which warrants additional studies.
Keywords: BRD4; renal tubular epithelial cells; senescence.
2024 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-24-214/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CAV1 Exacerbates Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Senescence by Suppressing CaMKK2/AMPK-Mediated Autophagy.Aging Cell. 2025 May;24(5):e14501. doi: 10.1111/acel.14501. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Aging Cell. 2025. PMID: 39887553 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular mechanisms of mycelium of Cordyceps sinensis ameliorating renal tubular epithelial cells aging induced by D-galactose via inhibiting autophagy-related AMPK/ULK1 signaling activation].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Mar;44(6):1258-1265. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20181205.001. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30989992 Chinese.
-
[Exploring molecular mechanisms of fucoidan in improving human proximal renal tubular epithelial cells aging by targeting autophagy signaling pathways].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Dec;45(24):6003-6011. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200709.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33496141 Chinese.
-
[Effect of p21 on the changes in renal tubular epithelial cells after ischemia/reperfusion injury of kidney].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2005 Oct;17(10):606-10. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2005. PMID: 16259919 Chinese.
-
Unlocking the secrets of aging: Epigenetic reader BRD4 as the target to combatting aging-related diseases.J Adv Res. 2024 Sep;63:207-218. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.11.006. Epub 2023 Nov 11. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37956861 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
