A contrast-enhanced computed tomography-based radiomics nomogram for preoperative differentiation between benign and malignant cystic renal lesions
- PMID: 38983472
- PMCID: PMC11228685
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-23-656
A contrast-enhanced computed tomography-based radiomics nomogram for preoperative differentiation between benign and malignant cystic renal lesions
Abstract
Background: There is lack of discrimination as to traditional imaging diagnostic methods of cystic renal lesions (CRLs). This study aimed to evaluate the value of machine learning models based on clinical data and contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) radiomics features in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant CRL.
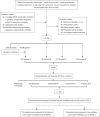
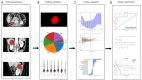
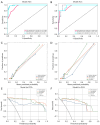
Methods: There were 192 patients with CRL (Bosniak class ≥ II) enrolled through histopathological examination, including 144 benign cystic renal lesions (BCRLs) and 48 malignant cystic renal lesions (MCRLs). Radiomics features were extracted from CECT images taken during the medullary phase. Using the light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM) algorithm, the clinical, radiomics and combined models were constructed. A comprehensive nomogram was developed by integrating the radiomics score (Rad-score) with independent clinical factors. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted. The corresponding area under the curve (AUC) value was worked out to quantify the discrimination performance of the three models in training and validation cohorts. Calibration curves were worked out to assess the accuracy of the probability values predicted by the models. Decision curve analysis (DCA) was worked out to assess the performance of models at different thresholds.
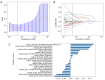
Results: Maximum diameter and Bosniak class were independent risk factors of patients with MCRL in the clinical model. Twenty-one radiomics features were extracted to work out a Rad-score. The performance of the clinical model in the training cohort was AUC =0.948, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.917-0.980, and the performance in the validation cohort was AUC =0.936, 95% CI: 0.859-1.000 (P<0.05). The performance of the radiomics model in the training cohort was AUC =0.990, 95% CI: 0.979-1.000, and the performance in the validation cohort was AUC =0.959, 95% CI: 0.903-1.000 (P<0.05). Compared with the above models, the combined radiomics nomogram had an AUC of 0.989 (95% CI: 0.977-1.000) in the training cohort and an AUC of 0.962 (95% CI: 0.905-1.000) in the validation cohort (P<0.05), showing the best diagnostic efficacy.
Conclusions: The radiomics nomogram integrating clinical independent risk factors and radiomics signature improved the diagnostic accuracy in differentiating between BCRL and MCRL, which can provide a reference for clinical decision-making and help clinicians develop individualized treatment strategies for patients.
Keywords: Bosniak classification; computed tomography (CT); cystic tumor; radiomics; renal cyst.
2024 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-23-656/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and validation of CT-based radiomics nomogram for the classification of benign parotid gland tumors.Med Phys. 2023 Feb;50(2):947-957. doi: 10.1002/mp.16042. Epub 2022 Nov 12. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36273307
-
Development and Validation of Contrast-Enhanced CT-Based Deep Transfer Learning and Combined Clinical-Radiomics Model to Discriminate Thymomas and Thymic Cysts: A Multicenter Study.Acad Radiol. 2024 Apr;31(4):1615-1628. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.10.018. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Acad Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37949702
-
A CT-based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of benign and malignant small renal masses (≤4 cm).Transl Oncol. 2023 Mar;29:101627. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101627. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36731307 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and verification of a prediction model based on clinical characteristics and computed tomography radiomics parameters for distinguishing benign and malignant pulmonary nodules.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Mar 29;16(3):1984-1995. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1400. Epub 2024 Mar 18. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 38617763 Free PMC article.
-
A CT-based radiomics nomogram involving the cystic fluid area for differentiating appendiceal mucinous neoplasms from appendicitis with intraluminal fluid.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Mar 20;150(3):143. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05695-5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38504073 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Radiomics for differential diagnosis of Bosniak II-IV renal masses via CT imaging.BMC Cancer. 2024 Dec 6;24(1):1508. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13283-6. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39643905 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
