Deep learning and optical coherence tomography in glaucoma: Bridging the diagnostic gap on structural imaging
- PMID: 38983522
- PMCID: PMC11182271
- DOI: 10.3389/fopht.2022.937205
Deep learning and optical coherence tomography in glaucoma: Bridging the diagnostic gap on structural imaging
Abstract
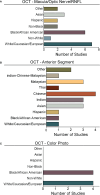
Glaucoma is a leading cause of progressive blindness and visual impairment worldwide. Microstructural evidence of glaucomatous damage to the optic nerve head and associated tissues can be visualized using optical coherence tomography (OCT). In recent years, development of novel deep learning (DL) algorithms has led to innovative advances and improvements in automated detection of glaucomatous damage and progression on OCT imaging. DL algorithms have also been trained utilizing OCT data to improve detection of glaucomatous damage on fundus photography, thus improving the potential utility of color photos which can be more easily collected in a wider range of clinical and screening settings. This review highlights ten years of contributions to glaucoma detection through advances in deep learning models trained utilizing OCT structural data and posits future directions for translation of these discoveries into the field of aging and the basic sciences.
Keywords: aging; artificial intelligence; basic sciences; deep learning; glaucoma; optical coherence tomography.
Copyright © 2022 Thompson, Falconi and Sappington.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

