The effect of remimazolam-based total intravenous anesthesia versus sevoflurane-based inhalation anesthesia on emergence delirium in children undergoing tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy: study protocol for a prospective randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 38983921
- PMCID: PMC11231196
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1373006
The effect of remimazolam-based total intravenous anesthesia versus sevoflurane-based inhalation anesthesia on emergence delirium in children undergoing tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy: study protocol for a prospective randomized controlled trial
Abstract
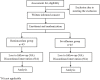
Background: Remimazolam, a new ultrashort-acting benzodiazepine, is becoming increasingly applied in general anesthesia. This study is designed to investigate the effect of remimazolam-based total intravenous anesthesia and sevoflurane-based inhalation anesthesia on emergence delirium in pediatric tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. Methods and analysis: This is a monocentric, prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. A total of 90 pediatric patients will be randomized to receive remimazolam-based total intravenous anesthesia (remimazolam group, n = 45) or sevoflurane-based inhalation anesthesia (sevoflurane group, n = 45). The primary outcome will be the incidence of emergence delirium, which will be evaluated using the Pediatric Anesthesia Emergence Delirium (PAED) scale. The secondary outcomes include the extubation time, recovery time, behavior change using the post-hospitalization behavior questionnaire for ambulatory surgery (PHBQ-AS), and adverse events. Ethics and dissemination: This study has been approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (2023-K-262-02). Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier NCT06214117.
Keywords: children; emergence delirium; general anesthesia; remimazolam; sevoflurane.
Copyright © 2024 Ma, Cai, Zhong, Chen, Wang, Lin, Wang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Remimazolam for the Prevention of Emergence Delirium in Children Following Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy Under Sevoflurane Anesthesia: A Randomized Controlled Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Sep 30;16:3413-3420. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S381611. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 36203819 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The safety and efficacy of remimazolam tosylate for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia in pediatric patients undergoing elective surgery: Study protocol for a multicenter, randomized, single-blind, positive-controlled clinical trial.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 10;14:1090608. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1090608. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36843931 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of intravenous and mask induction on post-operative emergence delirium in pediatric patients undergoing tonsillectomy with or without adenoidectomy.Ir J Med Sci. 2020 Aug;189(3):1061-1068. doi: 10.1007/s11845-020-02197-4. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Ir J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32048203 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of remimazolam tosilate for injection (HR7056) versus sevoflurane on the incidence of postoperative delirium in older patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty: study protocol for a prospective, multicentre, two-arm, parallel-group, randomised controlled trial.BMC Geriatr. 2025 Feb 18;25(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-05766-3. BMC Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 39966787 Free PMC article.
-
Concomitant Use of Intravenous Remimazolam With Inhalation Anesthesia and Subsequent Emergence Delirium in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2025 Mar 4;17(3):e80044. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80044. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40190846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chandler J. R., Myers D., Mehta D., Whyte E., Groberman M. K., Montgomery C. J., et al. (2013). Emergence delirium in children: a randomized trial to compare total intravenous anesthesia with propofol and remifentanil to inhalational sevoflurane anesthesia. Paediatr. Anaesth. 23, 309–315. 10.1111/pan.12090 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen J., Zou X., Hu B., Yang Y., Wang F., Zhou Q., et al. (2022). Effect of different doses of esketamine compared with fentanyl combined with propofol on hypotension in patients undergoing painless abortion surgery: a prospective, randomized, double-blind controlled clinical trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 22, 305. 10.1186/s12871-022-01848-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choi J. Y., Lee H. S., Kim J. Y., Han D. W., Yang J. Y., Kim M. J., et al. (2022). Comparison of remimazolam-based and propofol-based total intravenous anesthesia on postoperative quality of recovery: a randomized non-inferiority trial. J. Clin. Anesth. 82, 110955. 10.1016/j.jclinane.2022.110955 - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials