Recent trends: Retractions of articles in the oncology field
- PMID: 38984306
- PMCID: PMC11231537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33007
Recent trends: Retractions of articles in the oncology field
Abstract
Background: In recent years, there has been a surge in media reports on articles being retracted after publication. This issue has gained significant attention, particularly due to the consecutive large-scale retractions carried out by renowned international publishers, which have aroused widespread concern in the society.
Objective: To analyze the data of retracted articles and retraction trends.
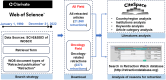
Methods: The publications were searched through Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database and imported into CiteSpace in plain text format, and visual analysis of countries, institutions, keywords, and subject areas were performed to reveal the trends of retracted articles and the worst areas of retraction.
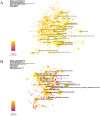
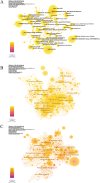
Results: From 1990 to 2022, 21,568 retracted articles were retrieved, among which the number of retracted articles increased year by year. China is the country with the highest number of retracted articles; Islamic Azad University is the institution with the highest number of retracted articles. In the analysis of all retracted articles across different subject areas, the number of retracted articles in the field of oncology was the highest; In the keyword cluster analysis of retracted articles within the field of oncology, the most prominent category of retracted articles were related to pancreatic cancer.
Conclusions: Scientific and systematic analysis of retracted articles is conducive to improving the quality of papers, raising the level of human research, and cleaning up the research environment.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis; CiteSpace; Retracted articles.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Research misconduct in health and life sciences research: A systematic review of retracted literature from Brazilian institutions.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 15;14(4):e0214272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214272. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30986211 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of retracted journal articles in the field of veterinary medicine and animal health.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Feb 18;18(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03167-x. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35180878 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted articles in scientific literature: A bibliometric analysis from 2003 to 2022 using the Web of Science.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 26;10(20):e38620. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38620. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39640756 Free PMC article.
-
Retractions in cancer research: a systematic survey.Res Integr Peer Rev. 2017 May 12;2:5. doi: 10.1186/s41073-017-0031-1. eCollection 2017. Res Integr Peer Rev. 2017. PMID: 29451549 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted articles in rehabilitation: just the tip of the iceberg? A bibliometric analysis.Arch Physiother. 2020 Nov 30;10(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40945-020-00092-w. Arch Physiother. 2020. PMID: 33292803 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Citation Contamination by Paper Mill Articles in Systematic Reviews of the Life Sciences.JAMA Netw Open. 2025 Jun 2;8(6):e2515160. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.15160. JAMA Netw Open. 2025. PMID: 40504528 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

