Screening tools to evaluate the neurotoxic potential of botanicals: building a strategy to assess safety
- PMID: 38984683
- PMCID: PMC11542175
- DOI: 10.1080/17425255.2024.2378895
Screening tools to evaluate the neurotoxic potential of botanicals: building a strategy to assess safety
Abstract
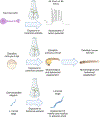
Areas covered: This paper outlines the selection of NAMs, including in vitro assays using primary rat cortical neurons, zebrafish embryos, and Caenorhabditis elegans. These assays aim to assess neurotoxic endpoints such as neuronal activity and behavioral responses. Microelectrode array recordings of rat cortical neurons provide insights into the impact of botanical extracts on neuronal function, while the zebrafish embryos and C. elegans assays evaluate neurobehavioral responses. The paper also provides an account of the selection of botanical case studies based on expert judgment and existing neuroactivity/toxicity information. The proposed battery of assays will be tested with these case studies to evaluate their utility for neurotoxicity screening.
Expert opinion: The complexity of botanicals necessitates the use of multiple NAMs for effective neurotoxicity screening. This paper discusses the evaluation of methodologies to develop a robust framework for evaluating botanical safety, including complex neuronal models and key neurodevelopmental process assays. It aims to establish a comprehensive screening framework.
Keywords: Botanical; NAM; UVCB; complex mixtures; in vitro; neurotoxicity; screening.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests:
P Spencer - Consultant, Shenzhen Center for Disease Control & Prevention, Shenzhen, PRC. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures

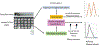

References
-
- Smith T, Resetar H, Morton C. US Sales of Herbal Supplements Increase by 9.7% in 2021. The Journal of the American Botanical Council. 2022;42–69.
-
- Houriet J, Vidar WS, Manwill PK, et al. How low can you go? Selecting intensity thresholds for untargeted metabolomics data preprocessing. Anal Chem. 2022;94:17964–17971. - PubMed
-
- Klaassen CD, Casarett LJ, Doull J, editors. Casarett and Doull’s toxicology: the basic science of poisons. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2013.
-
- Programme international sur la sécurité des substances chimiques, editor. Neurotoxicity risk assessment for human health: principles and approaches. Geneva: World health organization; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
