Efficacy and safety of infliximab and adalimumab in inflammatory bowel disease patients
- PMID: 38985232
- PMCID: PMC11416362
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-024-01508-w
Efficacy and safety of infliximab and adalimumab in inflammatory bowel disease patients
Abstract
Introduction: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), consists of two primary types: Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Crohn's Disease (CD). Infliximab (IFX) and Adalimumab (ADA) are frequently utilized in the management of moderate to severe cases of IBD.
Aim: This study aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of IFX and ADA in individuals diagnosed with moderate to severe IBD.
Method: This study is a prospective open-labeled randomized parallel study that included moderate to severe IBD patients treated with either IFX or ADA. A total of 56 patients participated, with 34 patients received IFX and 22 patients received ADA. Various measures, including Crohn's Disease Activity Index (CDAI), Mayo Score/ Disease Activity Index (DAI), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, were taken at baseline and week 14 to assess the efficacy of the treatments. In addition, the levels of drugs and sTREM-1 were measured at 14 weeks. Patient safety was monitored throughout the study period.
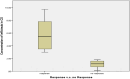
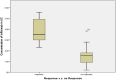
Results: In the group received IFX, there was a notable decrease in CDAI (P = 0.045), DAI (P = 0.026), and CRP (P = 0.023 for CD, and P = 0.021 for UC) levels. In addition, the group received ADA experienced a significant reduction in CDAI (P = 0.001), DAI (P = 0.032), and CRP (P < 0.018 for CD and P = 0.003 for UC) levels. Responders had higher drug concentrations than non-responders, notably IFX concentration was higher in responders with CD (P = 0.001) and UC (P < 0.001). ADA concentration was higher in UC (P <= 0.001) and all CD patients responded to the treatment. The same trend was observed for sTREM-1 levels in CD and UC patients (P = 0.042, and P = 0.015, respectively) in the IFX group. In UC patients treated with ADA, the level of sTREM-1 was significantly low (P = 0.002).
Conclusion: Both IFX and ADA have a good safety profile and deliver a beneficial clinical and laboratory response in moderate-severe IBD patients.
Clinical trial registration: This study is registered on ClinicalTrials.gov under the identifier NCT05291039. (You can access the study at https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05291039 (First Posted: March 22, 2022).
Keywords: Adalimumab; CDAI; DAI; Efficacy; Inflammatory bowel disease; Infliximab; Safety; sTREM-1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest were declared by the authors.
Figures



References
-
- Afif W, Leighton JA, Hanauer SB, Loftus EV Jr, Faubion WA, Pardi DS et al (2009) Open-label study of adalimumab in patients with ulcerative colitis including those with prior loss of response or intolerance to infliximab. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15(9):1302–1307 - PubMed
-
- Afify A, Gado M, Gohar M, Wadea F (2021) Clinical and biochemical response of treatment with anti-TNFα in egyptian IBD patients: zagazig university IBD clinic experience. Zagazig Univ Med J 10(4):56–78
-
- Cholapranee A, Hazlewood GS, Kaplan GG, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Ananthakrishnan AN (2017) Systematic review with meta-analysis: comparative efficacy of biologics for induction and maintenance of mucosal healing in crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis controlled trials. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 45(10):1291–1302 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
