The C-terminal sequences of Bcl-2 family proteins mediate interactions that regulate cell death
- PMID: 38985308
- PMCID: PMC11346437
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20210352
The C-terminal sequences of Bcl-2 family proteins mediate interactions that regulate cell death
Abstract
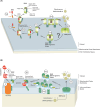
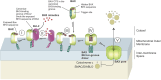
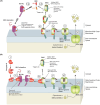
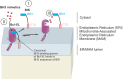
Programmed cell death via the both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways is regulated by interactions of the Bcl-2 family protein members that determine whether the cell commits to apoptosis via mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). Recently the conserved C-terminal sequences (CTSs) that mediate localization of Bcl-2 family proteins to intracellular membranes, have been shown to have additional protein-protein binding functions that contribute to the functions of these proteins in regulating MOMP. Here we review the pivotal role of CTSs in Bcl-2 family interactions including: (1) homotypic interactions between the pro-apoptotic executioner proteins that cause MOMP, (2) heterotypic interactions between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins that prevent MOMP, and (3) heterotypic interactions between the pro-apoptotic executioner proteins and the pro-apoptotic direct activator proteins that promote MOMP.
Keywords: BH3-only proteins; Bax; Bcl-2; apoptosis; protein–protein interactions; transmembrane domain.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

