The cerebellum modulates thirst
- PMID: 38987435
- PMCID: PMC12210242
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01700-9
The cerebellum modulates thirst
Abstract
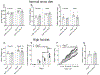
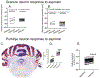
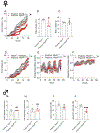
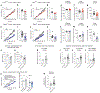
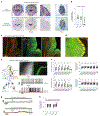
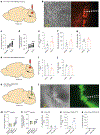
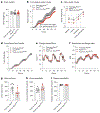
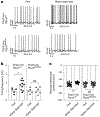
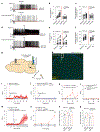
The cerebellum, a phylogenetically ancient brain region, has long been considered strictly a motor control structure. Recent studies have implicated the cerebellum in cognition, sensation, emotion and autonomic function, making it an important target for further investigation. Here, we show that cerebellar Purkinje neurons in mice are activated by the hormone asprosin, leading to enhanced thirst, and that optogenetic or chemogenetic activation of Purkinje neurons induces rapid manifestation of water drinking. Purkinje neuron-specific asprosin receptor (Ptprd) deletion results in reduced water intake without affecting food intake and abolishes asprosin's dipsogenic effect. Purkinje neuron-mediated motor learning and coordination were unaffected by these manipulations, indicating independent control of two divergent functions by Purkinje neurons. Our results show that the cerebellum is a thirst-modulating brain area and that asprosin-Ptprd signaling may be a potential therapeutic target for the management of thirst disorders.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
A.R.C. has been awarded asprosin-related patents and is a co-founder and equity holder of Aceragen and Recall Therapeutics. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




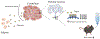

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK125403/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- DK102529/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 DK118290/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS119301/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK130931/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103555/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS127435/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DK118290/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- DK130931/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

