Isolation and characterisation of two epithelial-like cell lines from the gills of Chrysophrys auratus (Australasian snapper) and Oncorhynchus tshawytscha (Chinook salmon) and their use in aquatic toxicology
- PMID: 38987436
- PMCID: PMC12246032
- DOI: 10.1007/s11626-024-00941-z
Isolation and characterisation of two epithelial-like cell lines from the gills of Chrysophrys auratus (Australasian snapper) and Oncorhynchus tshawytscha (Chinook salmon) and their use in aquatic toxicology
Abstract
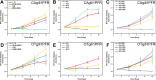
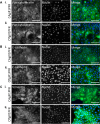
In vitro gill models are becoming increasingly important in aquatic toxicology, yet the fish gill invitrome is underrepresented, encompassing approximately 0.1% of extant species. Here, we describe the establishment and characterisation of two gill-derived, epithelial-like cell lines isolated from fish species of significant importance to New Zealand: Chrysophrys auratus (Australasian snapper) and Oncorhynchus tshawytscha (Chinook salmon). Designated CAgill1PFR (Chrysophrys auratus, gill 1, Plant & Food Research) and OTgill1PFR (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha, gill 1, Plant & Food Research), these cell lines have each been passaged greater than each 70 times over several years and are considered spontaneously immortalised. Both cell lines required serum for growth and exhibited differential responses to basal media formulations. CAgill1PFR was sensitive to low temperatures (4 °C) but replicated at high temperatures (30 °C), whereas OTgill1PFR was sensitive to high temperatures but remained viable at low temperatures, mirroring the natural environment of their host species. Immunostaining revealed expression of epithelial cell markers cytokeratin and E-cadherin, alongside positivity for the mesenchymal cell marker, vimentin. CAgill1PFR was more sensitive to the environmental toxin 3,4 dichloroaniline than OTgill1PFR through measurements of metabolic activity, membrane integrity, and lysosomal function. Furthermore, CAgill1PFR produced less CYP1A activity, indicative of ongoing biotransformation processes, in response to beta-naphthoflavone than OTgill1PFR. These cell lines expand the toolbox of resources and emphasise the need for species-specific aquatic toxicology research.
Keywords: 3,4 DCA; Australasian snapper; Chinook salmon; EROD; Epithelial; Toxicology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict Of Interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Abdul Majeed S, Nambi KSN, Taju G, Sarath Babu V, Farook MA, Sahul Hameed AS (2014) Development and characterization of a new gill cell line from air breathing fish Channa striatus (Bloch 1793) and its application in toxicology: Direct comparison to the acute fish toxicity. Chemosphere 96:89–98. 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.045 - PubMed
-
- Abdul Majeed S, Nambi KSN, Taju G, Sundar Raj N, Madan N, Sahul Hameed AS (2013) Establishment and characterization of permanent cell line from gill tissue of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) and its application in gene expression and toxicology. Cell Biol Toxicol 29:59–73. 10.1007/s10565-012-9237-7 - PubMed
-
- Aquaculture New Zealand (2024) Mussels & salmon set new export records in 2023. In: Neas M (ed) Aquaculture New Zealand Magazine. Available via https://www.aquaculture.org.nz/resources/magazine
-
- Araújo BC, Miller MR, Walker SP, Symonds JE (2023) The influence of temperature on performance, biological indices, composition, and nutrient retention of juvenile Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) reared in freshwater. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A Mol Integr Physiol 280:111412. 10.1016/j.cbpa.2023.111412 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

