Removal of contaminants of emerging concern by Wolffia arrhiza and Lemna minor depending on the process conditions, pollutants concentration, and matrix type
- PMID: 38987638
- PMCID: PMC11237155
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66962-6
Removal of contaminants of emerging concern by Wolffia arrhiza and Lemna minor depending on the process conditions, pollutants concentration, and matrix type
Abstract
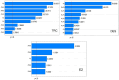
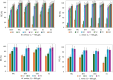
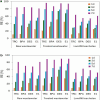
Research was carried out on the removal of a group of six contaminants of emerging concern: bisphenol A, N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide, diethylstilbestrol, triclosan, estrone and estradiol from the water matrix during contact with small floating macrophytes Wolffia arrhiza and Lemna minor. The optimal conditions for the process, such as pH, light exposure per day, and plant mass, were determined using the design of experiments chemometric approach based on central composite design. Experiments conducted under the designated optimal conditions showed that after 7 days, the removal efficiency equals 88-98% in the case of W. arrhiza and 87-97% in the case of L. minor, while after 14 days of the experiment, these values are 93-99.6% and 89-98%, respectively. The primary mechanism responsible for removing CECs is the plant uptake, with the mean uptake rate constant equal to 0.299 day-1 and 0.277 day-1 for W. arrhiza and L. minor, respectively. Experiments conducted using municipal wastewater as a sample matrix showed that the treatment efficiency remains high (the average values 84% and 75%; in the case of raw wastewater, 93% and 89%, and in the case of treated wastewater, for W. arrhiza and L. minor, respectively). Landfill leachate significantly reduces plants' ability to remove pollutants (the average removal efficiency equals 59% and 56%, for W. arrhiza and L. minor, respectively).
Keywords: Bisphenol A; DEET; Hormones; Landfill leachates; Phytoremediation; Removal mechanisms; Wastewater.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Kotowska U, Kapelewska J, Kotowski A, Pietuszewska E. Rapid and sensitive analysis of hormones and other emerging contaminants in groundwater using ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction with solidification of floating organic droplet followed by GC-MS detection. Water (Switzerland) 2019;11:1638.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

