Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells and Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 38988152
- PMCID: PMC11519824
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X22999240710142942
Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells and Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
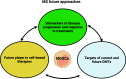
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs) are a heterogeneous population of immature myeloid cells that play important roles in maintaining immune homeostasis and regulating immune responses. MDSCs can be divided into two main subsets based on their surface markers and functional properties: granulocytic MDSCs (G-MDSCs) and monocytic MDSCs (M-MDSCs). Recently greatest attention has been paid to innate immunity in Multiple Sclerosis (MS), so the aim of our review is to provide an overview of the main characteristics of MDSCs in MS and its preclinical model by discussing the most recent data available. The immunosuppressive functions of MDSCs can be dysregulated in MS, leading to an exacerbation of the autoimmune response and disease progression. Antigen-specific peptide immunotherapy, which aims to restore tolerance while avoiding the use of non-specific immunosuppressive drugs, is a promising approach for autoimmune diseases, but the cellular mechanisms behind successful therapy remain poorly understood. Therefore, targeting MDSCs could be a promising therapeutic approach for MS. Various strategies for modulating MDSCs have been investigated, including the use of pharmacological agents, biological agents, and adoptive transfer of exogenous MDSCs. However, it remained unclear whether MDSCs display any therapeutic potential in MS and how this therapy could modulate different aspects of the disease. Collectively, all the described studies revealed a pivotal role for MDSCs in the regulation of MS.
Keywords: G-MDSCs; M-MDSCs; Multiple sclerosis; immune responses.; myeloid-derived suppressor cells; therapeutic strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical