Diffusion Tensor Imaging-Along the Perivascular-Space Index Is Associated with Disease Progression in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 38988232
- PMCID: PMC11524528
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.29908
Diffusion Tensor Imaging-Along the Perivascular-Space Index Is Associated with Disease Progression in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
Background: The glymphatic clearance pathway is a waste clearance system that allows for removal of soluble proteins such as amyloid β (Aβ) from the brain. Higher Aβ levels are associated with cognitive dysfunction in Parkinson's disease (PD). Diffusion tensor imaging-along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) is an imaging measure proposed to indirectly measure glymphatic function.
Objectives: Evaluate differences in DTI-ALPS-index between PD and healthy controls (HC) and characterize relationships between this proposed measure of glymphatic clearance, cognition, and disease severity in PD.
Methods: PD (n = 32) and HC (n = 23) participants underwent brain imaging to assess DTI-ALPS. PD participants were classified as PD-normal cognition (PD-NC; n = 20) or PD-mild cognitive impairment (PD-MCI; n = 12) based on a Level II comprehensive cognitive assessment. A subgroup of PD participants (n = 21) returned for annual assessments for up to 4 years after baseline. Longitudinal outcomes included changes in performance on the comprehensive cognitive assessment and changes in the Movement Disorders Society Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS).
Results: PD participants had lower DTI-ALPS-index compared to HC. PD participants classified as PD-MCI had significantly lower DTI-ALPS-index compared to PD-NC. Lower DTI-ALPS-index at baseline was associated with longitudinal cognitive decline and worse longitudinal disease severity.
Conclusions: Glymphatic clearance, as measured with DTI-ALPS, has potential to serve as a marker of longitudinal disease progression. Interventions targeting glymphatic function should be explored for potential to slow cognitive decline in PD. © 2024 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: DTI‐ALPS; Parkinson's disease; cognition; disease progression; glymphatic function.
© 2024 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
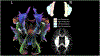
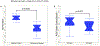
References
-
- Martinez-Martin P, Rodriguez-Blazquez C, Kurtis MM, Chaudhuri KR, Group NV. The impact of non-motor symptoms on health-related quality of life of patients with Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2011;26(3):399–406. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

