Partial wrapping of single-stranded DNA by replication protein A and modulation through phosphorylation
- PMID: 38989614
- PMCID: PMC11514480
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae584
Partial wrapping of single-stranded DNA by replication protein A and modulation through phosphorylation
Abstract
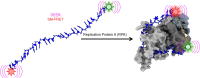
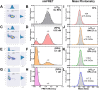
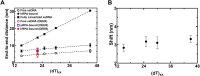
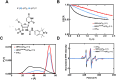
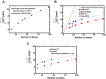
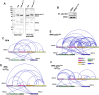
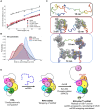
Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) intermediates which emerge during DNA metabolic processes are shielded by replication protein A (RPA). RPA binds to ssDNA and acts as a gatekeeper to direct the ssDNA towards downstream DNA metabolic pathways with exceptional specificity. Understanding the mechanistic basis for such RPA-dependent functional specificity requires knowledge of the structural conformation of ssDNA when RPA-bound. Previous studies suggested a stretching of ssDNA by RPA. However, structural investigations uncovered a partial wrapping of ssDNA around RPA. Therefore, to reconcile the models, in this study, we measured the end-to-end distances of free ssDNA and RPA-ssDNA complexes using single-molecule FRET and double electron-electron resonance (DEER) spectroscopy and found only a small systematic increase in the end-to-end distance of ssDNA upon RPA binding. This change does not align with a linear stretching model but rather supports partial wrapping of ssDNA around the contour of DNA binding domains of RPA. Furthermore, we reveal how phosphorylation at the key Ser-384 site in the RPA70 subunit provides access to the wrapped ssDNA by remodeling the DNA-binding domains. These findings establish a precise structural model for RPA-bound ssDNA, providing valuable insights into how RPA facilitates the remodeling of ssDNA for subsequent downstream processes.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
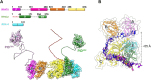

Update of
-
Wrapping of single-stranded DNA by Replication Protein A and modulation through phosphorylation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 29:2024.03.28.587234. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.28.587234. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 28;52(19):11626-11640. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae584. PMID: 38585962 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Wold M.S. Replication protein A: A heterotrimeric, single-stranded DNA-binding protein required for eukaryotic DNA metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997; 66:61–92. - PubMed
-
- Iftode C., Daniely Y., Borowiec J.A.. Replication protein A (RPA): the eukaryotic SSB. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999; 34:141–180. - PubMed
-
- Kim C., Paulus B.F., Wold M.S.. Interactions of human replication protein A with oligonucleotides. Biochemistry. 1994; 33:14197–14206. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35-GM149320/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 206708/Icelandic Research Fund
- 2072/22/Israeli Science Foundation
- R01 GM143179/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 CA290639/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM149320/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 GM144227/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RM1-GM144227/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- Estate of Gerald Alexander
- DE-SC0020965/Department of Energy
- Office of Basic Energy Sciences
- S10 OD030343/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103474/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

