Innovative construction of the first reliable catalogue of bovine circular RNAs
- PMID: 38989833
- PMCID: PMC11244336
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2024.2375090
Innovative construction of the first reliable catalogue of bovine circular RNAs
Abstract
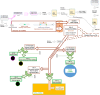
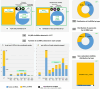
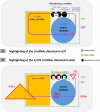
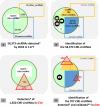
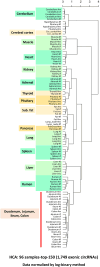
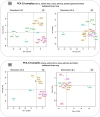
The aim of this study was to compare the circular transcriptome of divergent tissues in order to understand: i) the presence of circular RNAs (circRNAs) that are not exonic circRNAs, i.e. originated from backsplicing involving known exons and, ii) the origin of artificial circRNA (artif_circRNA), i.e. circRNA not generated in-vivo. CircRNA identification is mostly an in-silico process, and the analysis of data from the BovReg project (https://www.bovreg.eu/) provided an opportunity to explore new ways to identify reliable circRNAs. By considering 117 tissue samples, we characterized 23,926 exonic circRNAs, 337 circRNAs from 273 introns (191 ciRNAs, 146 intron circles), 108 circRNAs from small non-coding genes and nearly 36.6K circRNAs classified as other_circRNAs. Furthermore, for 63 of those samples we analysed in parallel data from total-RNAseq (ribosomal RNAs depleted prior to library preparation) with paired mRNAseq (library prepared with poly(A)-selected RNAs). The high number of circRNAs detected in mRNAseq, and the significant number of novel circRNAs, mainly other_circRNAs, led us to consider all circRNAs detected in mRNAseq as artificial. This study provided evidence of 189 false entries in the list of exonic circRNAs: 103 artif_circRNAs identified by total RNAseq/mRNAseq comparison using two circRNA tools, 26 probable artif_circRNAs, and 65 identified by deep annotation analysis. Extensive benchmarking was performed (including analyses with CIRI2 and CIRCexplorer-2) and confirmed 94% of the 23,737 reliable exonic circRNAs. Moreover, this study demonstrates the effectiveness of a panel of highly expressed exonic circRNAs (5-8%) in analysing the tissue specificity of the bovine circular transcriptome.
Keywords: Exonic circRNA; artificial annotation; artificial circRNA; backsplicing; bovine circRNAs; circular transcriptome; intron circle; lariat-derived circRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
In-Depth Analysis Reveals Production of Circular RNAs from Non-Coding Sequences.Cells. 2020 Jul 30;9(8):1806. doi: 10.3390/cells9081806. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32751504 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of pig transcriptomes suggests a global regulation mechanism enabling temporary bursts of circular RNAs.RNA Biol. 2019 Sep;16(9):1190-1204. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1621621. Epub 2019 Jun 3. RNA Biol. 2019. PMID: 31120323 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of the Circular Transcriptome in Muscle, Liver, and Testis in Three Livestock Species.Front Genet. 2021 May 10;12:665153. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.665153. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34040640 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Back Splicing, a Still Poorly Explored World: Non-Canonical Circular RNAs.Genes (Basel). 2020 Sep 22;11(9):1111. doi: 10.3390/genes11091111. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32972011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA Formation and Degradation Are Not Directed by Universal Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 16;26(2):726. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020726. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859439 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Salavati M, Clark R, Becker D, et al. Improving the annotation of the cattle genome by annotating transcription start sites in a diverse set of tissues and populations using cap analysis gene expression sequencing. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genet. 2023;13(8):G3 13. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkad108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
