Role of metabolic dysfunction and inflammation along the liver-brain axis in animal models with obesity-induced neurodegeneration
- PMID: 38989938
- PMCID: PMC11438328
- DOI: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01770
Role of metabolic dysfunction and inflammation along the liver-brain axis in animal models with obesity-induced neurodegeneration
Abstract
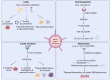
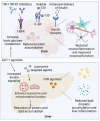
The interaction between metabolic dysfunction and inflammation is central to the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Obesity-related conditions like type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease exacerbate this relationship. Peripheral lipid accumulation, particularly in the liver, initiates a cascade of inflammatory processes that extend to the brain, influencing critical metabolic regulatory regions. Ceramide and palmitate, key lipid components, along with lipid transporters lipocalin-2 and apolipoprotein E, contribute to neuroinflammation by disrupting blood-brain barrier integrity and promoting gliosis. Peripheral insulin resistance further exacerbates brain insulin resistance and neuroinflammation. Preclinical interventions targeting peripheral lipid metabolism and insulin signaling pathways have shown promise in reducing neuroinflammation in animal models. However, translating these findings to clinical practice requires further investigation into human subjects. In conclusion, metabolic dysfunction, peripheral inflammation, and insulin resistance are integral to neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Understanding these complex mechanisms holds potential for identifying novel therapeutic targets and improving outcomes for neurodegenerative diseases.
Copyright © 2025 Copyright: © 2025 Neural Regeneration Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Alberghina M, Lupo G, Anfuso CD, Moro F. Palmitate transport through the blood-retina and blood-brain barrier of rat visual system during aging. Neurosci Lett. 1993;150:17–20. - PubMed
-
- Arruda AP, Milanski M, Coope A, Torsoni AS, Ropelle E, Carvalho DP, Carvalheira JB, Velloso LA. Low-grade hypothalamic inflammation leads to defective thermogenesis, insulin resistance, and impaired insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 2011;152:1314–1326. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

