Circulating Tumor DNA Assessment for Treatment Monitoring Adds Value to PSA in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 38990098
- PMCID: PMC11393539
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-1096
Circulating Tumor DNA Assessment for Treatment Monitoring Adds Value to PSA in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Enzalutamide after abiraterone progression is commonly used in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer despite a low rate of clinical benefit. Analyzing IMbassador250, a phase III trial assessing enzalutamide with or without atezolizumab after abiraterone, we hypothesized that baseline and early changes in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) tumor fraction (TF) may identify patients more likely to exhibit survival benefit from enzalutamide.
Experimental design: ctDNA was quantified from plasma samples using a tissue-agnostic assay without buffy coat sequencing. Baseline ctDNA TF, changes in ctDNA TF from baseline to cycle 3 day 1 (C3D1), and detection at C3D1 alone were compared with overall response rate, radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS), median OS (mOS), and 50% reduction in PSA.
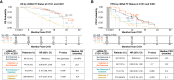
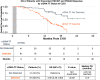
Results: ctDNA TF detection at baseline and/or C3D1 was associated with shorter rPFS and OS in 494 evaluable patients. Detection of ctDNA TF at C3D1, with or without detection at cycle 1 day 1, was associated with worse rPFS and mOS than lack of detection. When ctDNA TF and PSA response at C3D1 were discordant, patients with (ctDNA TF undetected/PSA not reduced) had more favorable outcomes than (ctDNA TF detected/PSA reduced; mOS 22.1 vs. 16 months; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: In a large cohort of patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer receiving enzalutamide after abiraterone, we demonstrate the utility of a new tissue-agnostic assay for monitoring molecular response based on ctDNA TF detection and dynamics. ctDNA TF provides a minimally invasive, complementary biomarker to PSA testing and may refine personalized treatment approaches.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
C.J. Sweeney reports grants and personal fees from Roche/Genentech, Astellas, and Pfizer, as well as personal fees from Merck, Bayer, BMS, Janssen, and Foundation Medicine Inc. during the conduct of the study. M. Childress reports other support from Foundation Medicine Inc. during the conduct of the study and from Foundation Medicine Inc. outside the submitted work, as well as stock in Roche. J. He reports other support from Foundation Medicine Inc. during the conduct of the study and from Foundation Medicine Inc. outside the submitted work, as well as stock ownership in Roche. D. Fabrizio reports other support from Foundation Medicine and Roche outside the submitted work. O. Gjoerup reports personal fees from Foundation Medicine Inc. and other support from Roche during the conduct of the study. S. Morley reports other support from Foundation Medicine Inc. during the conduct of the study and from Foundation Medicine Inc. outside the submitted work, as well as stock ownership in Roche Holdings AG. T. Catlett reports personal fees from Foundation Medicine Inc. during the conduct of the study and other support from Roche outside the submitted work. Z.J. Assaf reports other support from Roche/Genentech during the conduct of the study. K. Yuen reports personal fees from Genentech during the conduct of the study. M. Wongchenko reports other support from Genentech/Roche during the conduct of the study and from Genentech/Roche outside the submitted work. K. Shah reports other support from Genentech during the conduct of the study. P. Gupta reports other support from Roche/Genentech outside the submitted work. P. Hegde reports personal fees from Roche outside the submitted work. L.W. Pasquina reports other support from Foundation Medicine Inc. during the conduct of the study and from Foundation Medicine Inc. outside the submitted work, as well as stock ownership in Roche Holdings AG. S. Mariathasan reports employment at Genentech, a subsidiary of Roche. R.P. Graf reports other support from Foundation Medicine Inc. during the conduct of the study and from Foundation Medicine Inc. outside the submitted work. T. Powles reports grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, BMS, Exelixis, Ipsen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Merck Serono, Seattle Genetics, Astellas, Johnson & Johnson, Eisai, and Roche, as well as personal fees from Incyte and from Mashup outside the submitted work. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures



Comment in
-
Does circulating DNA tumor fraction add value to prostate-specific antigen in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer?Transl Cancer Res. 2025 May 30;14(5):2536-2538. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2025-295. Epub 2025 May 13. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40530150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Annala M, Fu S, Bacon JVW, Sipola J, Iqbal N, Ferrario C, et al. Cabazitaxel versus abiraterone or enzalutamide in poor prognosis metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase II trial. Ann Oncol 2021;32:896–905. - PubMed
-
- Annala M, Vandekerkhove G, Khalaf D, Taavitsainen S, Beja K, Warner EW, et al. Circulating tumor DNA genomics correlate with resistance to abiraterone and enzalutamide in prostate cancer. Cancer Discov 2018;8:444–57. - PubMed
-
- Tolmeijer SH, Boerrigter E, Schalken JA, Geerlings MJ, van Oort IM, van Erp NP, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the predictive value of cell-free DNA-based androgen receptor copy number gain in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. JCO Precis Oncol 2020;4:714–29. - PubMed
-
- George DJ, Sartor O, Miller K, Saad F, Tombal B, Kalinovský J, et al. Treatment patterns and outcomes in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in a real-world clinical practice setting in the United States. Clin Genitourin Cancer 2020;18:284–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

