Celecoxib inhibits NLRP1 inflammasome pathway in MDA-MB-231 Cells
- PMID: 38990306
- PMCID: PMC11522188
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-024-03286-2
Celecoxib inhibits NLRP1 inflammasome pathway in MDA-MB-231 Cells
Erratum in
-
Correction: Celecoxib inhibits NLRP1 inflammasome pathway in MDA-MB-231 Cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Nov;397(11):9205-9206. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03348-5. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39105800 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
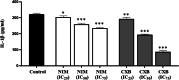
NLRP1 is predominantly overexpressed in breast cancer tissue, and the evaluated activation of NLRP1 inflammasome is associated with tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Therefore, targeting NLRP1 activation could be a crucial strategy in anticancer therapy. In this study, we investigated the hypothesis that NLRP1 pathway may contribute to the cytotoxic effects of celecoxib and nimesulide in MDA-MB-231 cells. First of all, IC50 values and inhibitory effects on the colony-forming ability of drugs were evaluated in cells. Then, the alterations in the expression levels of NLRP1 inflammasome components induced by drugs were investigated. Subsequently, the release of inflammatory cytokine IL-1β and the activity of caspase-1 in drug-treated cells were measured. According to our results, celecoxib and nimesulide selectively inhibited the viability of MDA-MB-231 cells. These drugs remarkably inhibited the colony-forming ability of cells. The expression levels of NLRP1 inflammasome components decreased in celecoxib-treated cells, accompanied by decreased caspase-1 activity and IL-1β release. In contrast, nimesulide treatment led to the upregulation of the related protein expressions with unchanged caspase-1 activity and increased IL-1β secretion. Our results indicated that the NLRP1 inflammasome pathway might contribute to the antiproliferative effects of celecoxib in MDA-MB-231 cells but is not a crucial mechanism for nimesulide.
Keywords: Anticancer drug; COX-2; Celecoxib; NLRP1 inflammasome; Triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
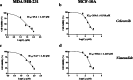
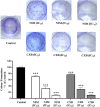
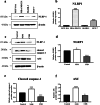
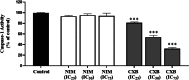
Similar articles
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin suppresses NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuronal death in ischemic stroke.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Sep 5;4(9):e790. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.326. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 24008734 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal NLRP1 inflammasome activation of Caspase-1 coordinately regulates inflammatory interleukin-1-beta production and axonal degeneration-associated Caspase-6 activation.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Oct;22(10):1676-86. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.16. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25744023 Free PMC article.
-
NLRC4, ASC and Caspase-1 Are Inflammasome Components that Are Mediated by P2Y2R Activation in Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 8;21(9):3337. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093337. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32397236 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP1 in Cutaneous SCCs: An Example of the Complex Roles of Inflammasomes in Cancer Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 14;23(20):12308. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012308. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The NLRP1 Inflammasome in Human Skin and Beyond.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 6;21(13):4788. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134788. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32640751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alle MD, Jones LJ (2015) The role of inflammation in the progression of breast cancer: friend or foe? (Review). Int J Oncol 47:797–805. 10.3892/ijo.2015.3075 - PubMed
-
- Ashok V, Dash C, Rohan TE, Sprafka JM, Terry PD (2011) Selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors and breast cancer risk. Breast 20:66–70. 10.1016/j.breast.2010.07.004 - PubMed
-
- Bennett A, Villa G (2000) Nimesulide: an NSAID that preferentially inhibits COX-2, and has various unique pharmacological activities. Expert Opin Pharmacother 1:277–286. 10.1517/14656566.1.2.277 - PubMed
-
- Bocca C, Bozzo F, Bassignana A, Miglietta A (2011) Antiproliferative effects of COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib on human breast cancer cell lines. Mol Cell Biochem 350:59–70. 10.1007/s11010-010-0682-4 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

