A bibliometric and visualization analysis of global research status and frontiers on autophagy in cardiomyopathies from 2004 to 2023
- PMID: 38990309
- PMCID: PMC11634079
- DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001876
A bibliometric and visualization analysis of global research status and frontiers on autophagy in cardiomyopathies from 2004 to 2023
Abstract
Background: Autophagy is intimately associated with the development of cardiomyopathy and has received widespread attention in recent years. However, no relevant bibliometric analysis is reported at present. In order to summarize the research status of autophagy in cardiomyopathy and provide direction for future research, we conducted a comprehensive, detailed, and multidimensional bibliometric analysis of the literature published in this field from 2004 to 2023.
Methods: All literatures related to autophagy in cardiomyopathy from 2004 to 2023 was collected from the Web of Science Core Collection, and annual papers, global publication trends, and proportion charts were analyzed and plotted using GraphPad price v8.0.2. In addition, CtieSpace [6.2.4R (64-bit) Advanced Edition] and VOSviewer (1.6.18 Edition) were used to analyze and visualize these data.
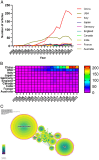
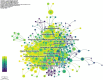
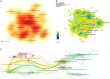
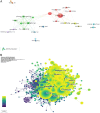
Results: Two thousand two hundred seventy-nine papers about autophagy in cardiomyopathy were accessed in the Web of Science Core Collection over the last 20 years, comprising literatures from 70 countries and regions, 2208 institutions, and 10 810 authors. China contributes 56.32% of the total publications, substantially surpassing other countries, while the United States is ranked first in frequency of citations. Among the top 10 authors, six are from China, and four are from the United States. Air Force Military Medical University was the institution with the highest number of publications, while the Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology (62 articles, 2.71% of the total) was the journal with the highest number of papers published in the field. Clustering of co-cited references and temporal clustering analysis showed that ferroptosis, hydrogen sulfide mitophagy, lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress, and SIRT1 are hot topics and trends in the field. The principal keywords are oxidative stress, heart, and heart failure.
Conclusion: The research on autophagy in cardiomyopathy is in the developmental stage. This represents the first bibliometric analysis of autophagy in cardiomyopathy, revealing the current research hotspots and future research directions in this field.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures





References
-
- Hollenberg SM, Singer M. Pathophysiology of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Cardiol 2021;18:424–434. - PubMed
-
- Zeng X, Zeng Q, Zhou L, et al. . Prevalence of chronic kidney disease among US adults with hypertension, 1999 to 2018. Hypertension 2023;80:2149–2158. - PubMed
-
- Bravo-San Pedro JM, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L. Autophagy and mitophagy in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 2017;120:1812–1824. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

