Preventing long-term disability in CIDP: the role of timely diagnosis and treatment monitoring in a multicenter CIDP cohort
- PMID: 38990346
- PMCID: PMC11377626
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-024-12548-1
Preventing long-term disability in CIDP: the role of timely diagnosis and treatment monitoring in a multicenter CIDP cohort
Abstract
Background: Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is an inflammatory disease affecting the peripheral nerves and the most frequent autoimmune polyneuropathy. Given the lack of established biomarkers or risk factors for the development of CIDP and patients' treatment response, this research effort seeks to identify potential clinical factors that may influence disease progression and overall treatment efficacy.
Methods: In this multicenter, retrospective analysis, we have screened 197 CIDP patients who presented to the University Hospitals in Düsseldorf, Berlin, Cologne, Essen, Magdeburg and Munich between 2018 and 2022. We utilized the respective hospital information system and examined baseline data with clinical examination, medical letters, laboratory results, antibody status, nerve conduction studies, imaging and biopsy findings. Aside from clinical baseline data, we analyzed treatment outcomes using the Standard of Care (SOC) definition, as well as a comparison of an early (within the first 12 months after manifestation) versus late (more than 12 months after manifestation) onset of therapy.
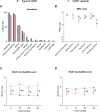
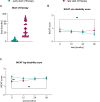
Results: In terms of treatment, most patients received intravenous immunoglobulin (56%) or prednisolone (39%) as their first therapy. Patients who started their initial treatment later experienced a worsening disease course, as reflected by a significant deterioration in their Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment (INCAT) leg disability score. SOC-refractory patients had worse clinical outcomes than SOC-responders. Associated factors for SOC-refractory status included the presence of fatigue as a symptom and alcohol dependence.
Conclusion: Timely diagnosis, prompt initiation of treatment and careful monitoring of treatment response are essential for the prevention of long-term disability in CIDP and suggest a "hit hard and early" treatment paradigm.
Keywords: Autoimmune; CIDP; Neuroimmunology; Therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MSc has received speaker honoraria from Alexion Pharmaceuticals, argenx, Bayer, Biogen, CSL Behring, Genzyme, Grifols, Merck, Miltenyi Biotec, Novartis, Roche, Teva, and Hormosan Pharma. He is vice chairman of the medical advisory board of the German Myasthenia Gravis Society. HPH received fees for serving on SC from Octapharma and Sanofi. MS served on the scientifc advisory boards and/or received speaker honoraria, travel funding or honoraria for medical writing from Argenex; Bayer; Biogen Idec; Biotest; CSL Behring; Genzyme; Grifols; Immunovant; Kedrion; Merck; Novartis; Octapharma; PPTA; Roche; Sanofi-Aventis; TEVA; UCB. FS received speaking honoria and honoria for attendance of advisory boards from argnx. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
CIDP Treatment Outcomes Correlation With First Nerve Conduction Changes: Ascertainment of Initial and Long-Term Responders.J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2025 Jun;30(2):e70017. doi: 10.1111/jns.70017. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2025. PMID: 40189868
-
Subcutaneous immunoglobulin for maintenance treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (The PATH Study): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2016 Jul 25;17(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s13063-016-1466-2. Trials. 2016. PMID: 27455854 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Maintenance Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy: 18-Month Post-marketing Surveillance in 103 Patients.Intern Med. 2025 Feb 15;64(4):535-541. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.3661-24. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39019607 Free PMC article.
-
Childhood chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuroradiculopathy--three cases and a review of the literature.Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2012 Jul;16(4):315-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2011.12.003. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22225859 Review.
-
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: prognosis and outcome.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005 Dec;35(3):175-84. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2005.08.008. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005. PMID: 16325658 Review.
Cited by
-
Determinants of long-term disability in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: A multicenter Korea/UK study of 144 patients.Eur J Neurol. 2025 Jan;32(1):e16575. doi: 10.1111/ene.16575. Eur J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39654304 Free PMC article.
-
Endoneurial immune interplay in peripheral nerve repair: insights and implications for future therapeutic interventions.Front Neurosci. 2025 May 9;19:1602112. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1602112. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40415889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Social Deprivation on Diagnosis, Management and Outcome of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy at a Tertiary UK Centre.J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2025 Sep;30(3):e70054. doi: 10.1111/jns.70054. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2025. PMID: 40801213 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker for CIDP Diagnosis, Severity, and Treatment Outcome.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2025 Jul;12(4):e200419. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200419. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2025. PMID: 40472292 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

