Mind the gap in kidney care: translating what we know into what we do
- PMID: 38991207
- PMCID: PMC11239182
- DOI: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2024-E007en
Mind the gap in kidney care: translating what we know into what we do
Abstract
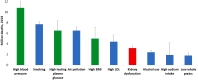
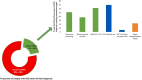
Historically, it takes an average of 17 years for new treatments to move from clinical evidence to daily practice. Given the highly effective treatments now available to prevent or delay kidney disease onset and progression, this is far too long. Now is the time to narrow the gap between what we know and what we do. Clear guidelines exist for the prevention and management of common risk factors for kidney disease, such as hypertension and diabetes, but only a fraction of people with these conditions are diagnosed worldwide, and even fewer are treated to target. Similarly, the vast majority of people living with kidney disease are unaware of their condition, because it is often silent in the early stages. Even among patients who have been diagnosed, many do not receive appropriate treatment for kidney disease. Considering the serious consequences of kidney disease progression, kidney failure, or death, it is imperative that treatments are initiated early and appropriately. Opportunities to diagnose and treat kidney disease early must be maximized beginning at the primary care level. Many systematic barriers exist, ranging from the patient to the clinician to the health systems to societal factors. To preserve and improve kidney health for everyone everywhere, each of these barriers must be acknowledged so that sustainable solutions are developed and implemented without further delay.
Resumo: Historicamente, são necessários, em média, 17 anos para que novos tratamentos passem da evidência clínica para a prática diária. Considerando os tratamentos altamente eficazes disponíveis atualmente para prevenir ou retardar o início e a progressão da doença renal, esse período é demasiadamente longo. Agora é o momento de reduzir a lacuna entre o que sabemos e aquilo que fazemos. Existem diretrizes claras para a prevenção e o manejo dos fatores de risco comuns para doenças renais, como hipertensão e diabetes, mas apenas uma fração das pessoas com essas condições é diagnosticada mundialmente, e um número ainda menor recebe tratamento adequado. Da mesma forma, a grande maioria das pessoas que sofrem de doença renal não têm conhecimento de sua condição, pois ela costuma ser silenciosa nos estágios iniciais. Mesmo entre pacientes que foram diagnosticados, muitos não recebem tratamento adequado para a doença renal. Levando em consideração as graves consequências da progressão da doença renal, insuficiência renal ou óbito, é imperativo que os tratamentos sejam iniciados precocemente e de maneira adequada. As oportunidades para diagnosticar e tratar precocemente a doença renal devem ser maximizadas, começando no nível da atenção primária. Existem muitas barreiras sistemáticas, que vão desde o paciente até o médico, passando pelos sistemas de saúde e por fatores sociais. Para preservar e melhorar a saúde renal para todos em qualquer lugar, cada uma dessas barreiras deve ser reconhecida para que soluções sustentáveis sejam desenvolvidas e implementadas sem mais demora.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mind the gap in kidney care: Translating what we know into what we do.Nephrology (Carlton). 2025 Jan;30(1):e14314. doi: 10.1111/nep.14314. Nephrology (Carlton). 2025. PMID: 39789717 Free PMC article.
-
Mind the gap in kidney care: translating what we know into what we do.Nephrol Ther. 2024 Jun;20(3):164-175. doi: 10.1684/ndt.2024.80. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Nephrol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38864256 English.
-
Mind the gap in kidney care: translating what we know into what we do.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024 Sep;28(9):835-846. doi: 10.1007/s10157-024-02518-2. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38970648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mind the gap in kidney care: Translating what we know into what we do.Clin Nephrol. 2024 Aug;102(2):59-72. doi: 10.5414/CNWKDEdi24. Clin Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38818714
-
Mind the gap in kidney care: Translating what we know into what we do.Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2024 Sep-Oct;44(5):731-742. doi: 10.1016/j.nefroe.2024.11.004. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2024. PMID: 39547779 Review.
References
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation . GBD compare data visualization [Internet] 2023. [[cited 2023 Nov 18] ]. Available from: http://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare.
-
- International Society of Nephrology . ISN global kidney health atlas [Internet] 3. Belgium: ISN; 2023. [[cited 2023 Nov 18]]. Available from: https://www.theisn.org/initiatives/global-kidney-health-atlas/
-
- Bikbov B, Purcell CA, Levey AS, Smith M, Abdoli A, Abebe M, et al. GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2020;395(10225):709–33. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

