Plasma metabolomics of immune-related adverse events for patients with lung cancer treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors
- PMID: 38991728
- PMCID: PMC11243122
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009399
Plasma metabolomics of immune-related adverse events for patients with lung cancer treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Metabolomics has the characteristics of terminal effects and reflects the physiological state of biological diseases more directly. Several current biomarkers of multiple omics were revealed to be associated with immune-related adverse events (irAEs) occurrence. However, there is a lack of reliable metabolic biomarkers to predict irAEs. This study aims to explore the potential metabolic biomarkers to predict risk of irAEs and to investigate the association of plasma metabolites level with survival in patients with lung cancer receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor treatment.
Methods: The study collected 170 plasmas of 85 patients with lung cancer who received immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) treatment. 58 plasma samples of 29 patients with irAEs were collected before ICIs treatment and at the onset of irAEs. 112 plasma samples of 56 patients who did not develop irAEs were collected before ICIs treatment and plasma matched by treatment cycles to onset of irAEs patients. Untargeted metabolomics analysis was used to identify the differential metabolites before initiating ICIs treatment and during the process that development of irAEs. Kaplan-Meier curves analysis was used to detect the associations of plasma metabolites level with survival of patients with lung cancer.
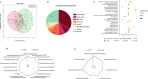
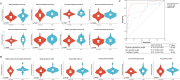
Results: A total of 24 differential metabolites were identified to predict the occurrence of irAEs. Baseline acylcarnitines and steroids levels are significantly higher in patients with irAEs, and the model of eight acylcarnitine and six steroid metabolites baseline level predicts irAEs occurrence with area under the curve of 0.91. Patients with lower concentration of baseline decenoylcarnitine(AcCa(10:1) 2, decenoylcarnitine(AcCa(10:1) 3 and hexanoylcarnitine(AcCa(6:0) in plasma would have better overall survival (OS). Moreover, 52 differential metabolites were identified related to irAEs during ICIs treatment, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, corticoserone, cortisol, thyroxine and sphinganine 1-phaosphate were significantly decreased in irAEs group while oxoglutaric acid and taurocholic acid were significantly increased in irAEs group.
Conclusions: High levels of acylcarnitines and steroid hormone metabolites might be risk factor to development of irAEs, and levels of decenoylcarnitine (AcCa(10:1) 2, decenoylcarnitine (AcCa(10:1) 3 and hexanoylcarnitine (AcCa(6:0) could be used to predict OS for patients with lung cancer received ICIs treatment.
Keywords: Biomarker; Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor; Lung Cancer.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Peripheral Blood Markers Identify Risk of Immune-Related Toxicity in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors.Oncologist. 2019 Aug;24(8):1128-1136. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0563. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 31015312 Free PMC article.
-
Serum IL-6 predicts immunotherapy-related adverse and outcome in advanced gastric and esophageal cancer patients with Anti-PD-1 treatment.Front Immunol. 2025 May 30;16:1553882. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1553882. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40519900 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Multisystem Immune-related Adverse Events and Progression-free Survivals in PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitor Monotherapy.In Vivo. 2024 Nov-Dec;38(6):2886-2896. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13770. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 39477436 Free PMC article.
-
[Current Status and Prospect of PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Elderly Patients with Advanced NSCLC].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024 May 20;27(5):367-375. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2024.106.10. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38880924 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Effectivity and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for different level of PD-L1-positive, advanced NSCLC: A meta-analysis of 4939 patients from randomized controlled trials.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jul;84:106452. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106452. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32339922
Cited by
-
Immunometabolism: The role of gut-derived microbial metabolites in optimising immune response during checkpoint inhibitor therapy.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Sep;15(9):e70472. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70472. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40910376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomics- and Proteomics-Based Disease Diagnostic Classifier Model for the Prediction and Diagnosis of Colorectal Carcinoma.J Proteome Res. 2025 Apr 4;24(4):2096-2111. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5c00010. Epub 2025 Mar 19. J Proteome Res. 2025. PMID: 40108892
-
Application of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer.MedComm (2020). 2025 Aug 10;6(8):e70176. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70176. eCollection 2025 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40787068 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
