Get Ready to Sharpen Your Tools: A Short Guide to Heterotrimeric G Protein Activity Biosensors
- PMID: 38991745
- PMCID: PMC11331509
- DOI: 10.1124/molpharm.124.000949
Get Ready to Sharpen Your Tools: A Short Guide to Heterotrimeric G Protein Activity Biosensors
Abstract
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest class of transmembrane receptors encoded in the human genome, and they initiate cellular responses triggered by a plethora of extracellular stimuli ranging from neurotransmitters and hormones to photons. Upon stimulation, GPCRs activate heterotrimeric G proteins (Gαβγ) in the cytoplasm, which then convey signals to their effectors to elicit cellular responses. Given the broad biological and biomedical relevance of GPCRs and G proteins in physiology and disease, there is great interest in developing and optimizing approaches to measure their signaling activity with high accuracy and across experimental systems pertinent to their functions in cellular communication. This review provides a historical perspective on approaches to measure GPCR-G protein signaling, from quantification of second messengers and other indirect readouts of activity to biosensors that directly detect the activity of G proteins. The latter is the focus of a more detailed overview of the evolution of design principles for various optical biosensors of G protein activity with different experimental capabilities. We will highlight advantages and limitations of biosensors that detect different G protein activation hallmarks, like dissociation of Gα and Gβγ or nucleotide exchange on Gα, as well as their suitability to detect signaling mediated by endogenous versus exogenous signaling components or in physiologically relevant systems like primary cells. Overall, this review intends to provide an assessment of the state-of-the-art for biosensors that directly measure G protein activity to allow readers to make informed decisions on the selection and implementation of currently available tools. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: G protein activity biosensors have become essential and widespread tools to assess GPCR signaling and pharmacology. Yet, investigators face the challenge of choosing from a growing list of G protein activity biosensors. This review provides an overview of the features and capabilities of different optical biosensor designs for the direct detection of G protein activity in cells, with the aim of facilitating the rational selection of systems that align with the specific scientific questions and needs of investigators.
Copyright © 2024 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures
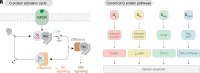
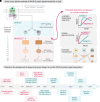

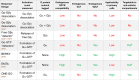
References
-
- Akgoz M, Kalyanaraman V, Gautam N (2004) Receptor-mediated reversible translocation of the G protein betagamma complex from the plasma membrane to the Golgi complex. J Biol Chem 279:51541–51544. - PubMed
-
- Audet N, Galés C, Archer-Lahlou E, Vallières M, Schiller PW, Bouvier M, Pineyro G (2008) Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer assays reveal ligand-specific conformational changes within preformed signaling complexes containing delta-opioid receptors and heterotrimeric G proteins. J Biol Chem 283:15078–15088. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
