Keep calm and reboot - how cells restart transcription after DNA damage and DNA repair
- PMID: 38991979
- PMCID: PMC11771587
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.14964
Keep calm and reboot - how cells restart transcription after DNA damage and DNA repair
Abstract
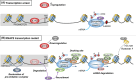
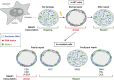
The effects of genotoxic agents on DNA and the processes involved in their removal have been thoroughly studied; however, very little is known about the mechanisms governing the reinstatement of cellular activities after DNA repair, despite restoration of the damage-induced block of transcription being essential for cell survival. In addition to impeding transcription, DNA lesions have the potential to disrupt the precise positioning of chromatin domains within the nucleus and alter the meticulously organized architecture of the nucleolus. Alongside the necessity of resuming transcription mediated by RNA polymerase 1 and 2 transcription, it is crucial to restore the structure of the nucleolus to facilitate optimal ribosome biogenesis and ensure efficient and error-free translation. Here, we examine the current understanding of how transcriptional activity from RNA polymerase 2 is reinstated following DNA repair completion and explore the mechanisms involved in reassembling the nucleolus to safeguard the correct progression of cellular functions. Given the lack of information on this vital function, this Review seeks to inspire researchers to explore deeper into this specific subject and offers essential suggestions on how to investigate this complex and nearly unexplored process further.
Keywords: DNA repair; RNA polymerase 1; RNA polymerase 2; UV lesions; chromatin; homeostasis; nucleolus.
© 2024 The Author(s). FEBS Letters published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Traveling Rocky Roads: The Consequences of Transcription-Blocking DNA Lesions on RNA Polymerase II.J Mol Biol. 2017 Oct 27;429(21):3146-3155. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Nov 13. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27851891 Review.
-
Nucleolus: A Central Hub for Nuclear Functions.Trends Cell Biol. 2019 Aug;29(8):647-659. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Trends Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31176528 Review.
-
STK19 drives transcription-coupled repair by stimulating repair complex stability, RNA Pol II ubiquitylation, and TFIIH recruitment.Mol Cell. 2024 Dec 19;84(24):4740-4757.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.10.030. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39547223
-
Active mRNA degradation by EXD2 nuclease elicits recovery of transcription after genotoxic stress.Nat Commun. 2023 Jan 20;14(1):341. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35922-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36670096 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between the nucleolus and the DNA damage response.Mol Biosyst. 2017 Feb 28;13(3):443-455. doi: 10.1039/c6mb00740f. Mol Biosyst. 2017. PMID: 28112326 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription-Coupled Repair and R-Loop Crosstalk in Genome Stability.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 16;26(8):3744. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083744. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanical Forces, Nucleus, Chromosomes, and Chromatin.Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 1;15(3):354. doi: 10.3390/biom15030354. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kuper J and Kisker C (2023) At the core of nucleotide excision repair. Curr Opin Struct Biol 80, 102605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

