Hyperconfined bio-inspired Polymers in Integrative Flow-Through Systems for Highly Selective Removal of Heavy Metal Ions
- PMID: 38992009
- PMCID: PMC11239941
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49869-8
Hyperconfined bio-inspired Polymers in Integrative Flow-Through Systems for Highly Selective Removal of Heavy Metal Ions
Abstract
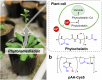
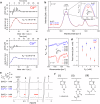
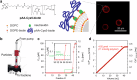
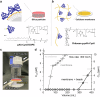
Access to clean water, hygiene, and sanitation is becoming an increasingly pressing global demand, particularly owing to rapid population growth and urbanization. Phytoremediation utilizes a highly conserved phytochelatin in plants, which captures hazardous heavy metal ions from aquatic environments and sequesters them in vacuoles. Herein, we report the design of phytochelatin-inspired copolymers containing carboxylate and thiolate moieties. Titration calorimetry results indicate that the coexistence of both moieties is essential for the excellent Cd2+ ion-capturing capacity of the copolymers. The obtained dissociation constant, KD ~ 1 nM for Cd2+ ion, is four-to-five orders of magnitude higher than that for peptides mimicking the sequence of endogenous phytochelatin. Furthermore, infrared and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy results unravel the mechanism underlying complex formation at the molecular level. The grafting of 0.1 g bio-inspired copolymers onto silica microparticles and cellulose membranes helps concentrate the copolymer-coated microparticles in ≈3 mL volume to remove Cd2+ ions from 0.3 L of water within 1 h to the drinking water level (<0.03 µM). The obtained results suggest that hyperconfinement of bio-inspired polymers in flow-through systems can be applied for the highly selective removal of harmful contaminants from the environmental water.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Poly(methacrylate citric acid) with good biosafety as nanoadsorbents of heavy metal ions.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020 Mar;187:110656. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110656. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020. PMID: 31796243
-
Imprinted polymers for the removal of heavy metal ions from water.Water Sci Technol. 2011;64(6):1325-32. doi: 10.2166/wst.2011.423. Water Sci Technol. 2011. PMID: 22214087
-
Continuous fixed-bed column study and adsorption modeling removal of Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ ions from synthetic acid mine drainage by nanocomposite cellulose hydrogel.J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2022;57(2):117-129. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2022.2036552. Epub 2022 Feb 9. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2022. PMID: 35137674
-
Phytochelatins: peptides involved in heavy metal detoxification.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2010 Mar;160(3):945-63. doi: 10.1007/s12010-009-8565-4. Epub 2009 Feb 18. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 19224399 Review.
-
Cytotoxic aquatic pollutants and their removal by nanocomposite-based sorbents.Chemosphere. 2020 Nov;258:127324. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127324. Epub 2020 Jun 7. Chemosphere. 2020. PMID: 32544812 Review.
Cited by
-
A Disila[2]ferrocenophane with a Bridging 9,9'-Bi-9H-9-Silafluorene Moiety.Molecules. 2025 Mar 18;30(6):1361. doi: 10.3390/molecules30061361. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40142137 Free PMC article.
-
High-performance QM/MM Enhanced Sampling Molecular Dynamics Simulations with GENESIS SPDYN and QSimulate-QM.J Chem Theory Comput. 2025 Apr 22;21(8):4016-4029. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.5c00163. Epub 2025 Apr 2. J Chem Theory Comput. 2025. PMID: 40174884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Islam, R., Rahman, M. S. Sustainable Water Purification 1st edn, 352 (John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken, 2020).
-
- Qasem NAA, Mohammed RH, Lawal DU. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: a comprehensive and critical review. npj Clean Water. 2021;4:36. doi: 10.1038/s41545-021-00127-0. - DOI
-
- Werber JR, Osuji CO, Elimelech M. Materials for next-generation desalination and water purification membranes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016;1:16018. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2016.18. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

