Assessing accuracy and consistency in intracranial aneurysm sizing: human expertise vs. artificial intelligence
- PMID: 38992041
- PMCID: PMC11239926
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-65825-4
Assessing accuracy and consistency in intracranial aneurysm sizing: human expertise vs. artificial intelligence
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Assessing accuracy and consistency in intracranial aneurysm sizing: human expertise vs. artificial intelligence.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 6;14(1):18233. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69217-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39107473 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
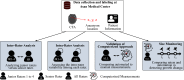
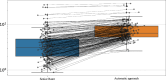
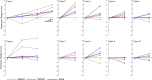
Intracranial aneurysms (IAs) are a common vascular pathology and are associated with a risk of rupture, which is often fatal. Aneurysm growth of more than 1 mm is considered a surrogate of rupture risk, therefore, this study presents a comprehensive analysis of intracranial aneurysm measurements utilizing a dataset comprising 358 IA from 248 computed tomography angiography (CTA) scans measured by four junior raters and one senior rater. The study explores the variability in sizing assessments by employing both human raters and an Artificial Intelligence (AI) system. Our findings reveal substantial inter- and intra-rater variability among junior raters, contrasting with the lower intra-rater variability observed in the senior rater. Standard deviations of all raters were above the threshold for IA growth (1 mm). Additionally, the study identifies a systemic bias, indicating a tendency for human experts to measure aneurysms smaller than the AI system. Our findings emphasize the challenges in human assessment while also showcasing the capacity of AI technology to improve the precision and reliability of intracranial aneurysm assessments, especially beneficial for junior raters. The potential of AI was particularly evident in the task of monitoring IA at various intervals, where the AI-based approach surpassed junior raters and achieved performance comparable to senior raters.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Dimmick, S., Jones, M., Steinfort, B., Pines, C. & Faulder, K. Accuracy and interobserver reliability of three-dimensional rotational angiography versus mathematical models for volumetric measurement of intracranial aneurysms. J. Clin. Neurosci.16, 1195–1198 (2009). 10.1016/j.jocn.2008.11.011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Forbes, G., Fox, A. J., Huston, J., Wiebers, D. O. & Torner, J. Interobserver variability in angiographic measurement and morphologic characterization of intracranial aneurysms: a report from the international study of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Am. J. Neuroradiol.17, 1407–1415 (1996). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

