Synthetic macrolides overcoming MLSBK-resistant pathogens
- PMID: 38992047
- PMCID: PMC11239830
- DOI: 10.1038/s41421-024-00702-y
Synthetic macrolides overcoming MLSBK-resistant pathogens
Abstract
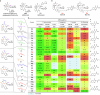
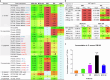
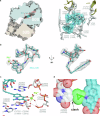
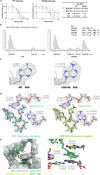
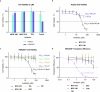
Conventional macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B-ketolide (MLSBK) antibiotics are unable to counter the growing challenge of antibiotic resistance that is conferred by the constitutive methylation of rRNA base A2058 or its G2058 mutation, while the presence of unmodified A2058 is crucial for high selectivity of traditional MLSBK in targeting pathogens over human cells. The absence of effective modes of action reinforces the prevailing belief that constitutively antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus remains impervious to existing macrolides including telithromycin. Here, we report the design and synthesis of a novel series of macrolides, featuring the strategic fusion of ketolide and quinolone moieties. Our effort led to the discovery of two potent compounds, MCX-219 and MCX-190, demonstrating enhanced antibacterial efficacy against a broad spectrum of formidable pathogens, including A2058-methylated Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, and notably, the clinical Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolates harboring A2058G mutations which are implicated in the recent pneumonia outbreak in China. Mechanistic studies reveal that the modified quinolone moiety of MCX-190 establishes a distinctive secondary binding site within the nascent peptide exit tunnel. Structure-activity relationship analysis underscores the importance of this secondary binding, maintained by a sandwich-like π-π stacking interaction and a water-magnesium bridge, for effective engagement with A2058-methylated ribosomes rather than topoisomerases targeted by quinolone antibiotics. Our findings not only highlight MCX-219 and MCX-190 as promising candidates for next-generation MLSBK antibiotics to combat antibiotic resistance, but also pave the way for the future rational design of the class of MLSBK antibiotics, offering a strategic framework to overcome the challenges posed by escalating antibiotic resistance.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

