The glycine-rich domain of GRP7 plays a crucial role in binding long RNAs and facilitating phase separation
- PMID: 38992080
- PMCID: PMC11239674
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66955-5
The glycine-rich domain of GRP7 plays a crucial role in binding long RNAs and facilitating phase separation
Abstract
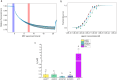
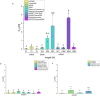
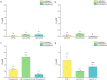
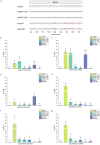
Microscale thermophoresis (MST) is a well-established method to quantify protein-RNA interactions. In this study, we employed MST to analyze the RNA binding properties of glycine-rich RNA binding protein 7 (GRP7), which is known to have multiple biological functions related to its ability to bind different types of RNA. However, the exact mechanism of GRP7's RNA binding is not fully understood. While the RNA-recognition motif of GRP7 is known to be involved in RNA binding, the glycine-rich region (known as arginine-glycine-glycine-domain or RGG-domain) also influences this interaction. To investigate to which extend the RGG-domain of GRP7 is involved in RNA binding, mutation studies on putative RNA interacting or modulating sites were performed. In addition to MST experiments, we examined liquid-liquid phase separation of GRP7 and its mutants, both with and without RNA. Furthermore, we systemically investigated factors that might affect RNA binding selectivity of GRP7 by testing RNAs of different sizes, structures, and modifications. Consequently, our study revealed that GRP7 exhibits a high affinity for a variety of RNAs, indicating a lack of pronounced selectivity. Moreover, we established that the RGG-domain plays a crucial role in binding longer RNAs and promoting phase separation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
JACALIN-LECTIN LIKE1 Regulates the Nuclear Accumulation of GLYCINE-RICH RNA-BINDING PROTEIN7, Influencing the RNA Processing of FLOWERING LOCUS C Antisense Transcripts and Flowering Time in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2015 Nov;169(3):2102-17. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00801. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26392261 Free PMC article.
-
Phase separation of GRP7 facilitated by FERONIA-mediated phosphorylation inhibits mRNA translation to modulate plant temperature resilience.Mol Plant. 2024 Mar 4;17(3):460-477. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2024.02.001. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Mol Plant. 2024. PMID: 38327052
-
Cold shock domain proteins and glycine-rich RNA-binding proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana can promote the cold adaptation process in Escherichia coli.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(2):506-16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl1076. Epub 2006 Dec 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17169986 Free PMC article.
-
The RGG motif proteins: Interactions, functions, and regulations.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Jan;14(1):e1748. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1748. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 35661420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RGG/RG Motif Regions in RNA Binding and Phase Separation.J Mol Biol. 2018 Nov 2;430(23):4650-4665. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.06.014. Epub 2018 Jun 15. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29913160 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the Role of AtGRP7 Arginine 141, a Target of Dimethylation by PRMT5, in Flowering Time Control and Stress Response.Plants (Basel). 2024 Oct 3;13(19):2771. doi: 10.3390/plants13192771. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409642 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicular and non-vesicular extracellular small RNAs direct gene silencing in a plant-interacting bacterium.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 14;16(1):3533. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57908-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40229238 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

