Benmelstobart, anlotinib and chemotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: a randomized phase 3 trial
- PMID: 38992123
- PMCID: PMC11485241
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03132-1
Benmelstobart, anlotinib and chemotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: a randomized phase 3 trial
Abstract
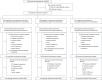
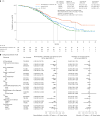
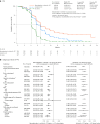
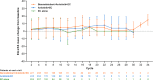
Immunochemotherapy is the first-line standard for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). Combining the regimen with anti-angiogenesis may improve efficacy. ETER701 was a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial that investigated the efficacy and safety of benmelstobart (a novel programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitor) with anlotinib (a multi-target anti-angiogenic small molecule) and standard chemotherapy in treatment-naive ES-SCLC. The ETER701 trial assessed two primary endpoints: Independent Review Committee-assessed progression-free survival per RECIST 1.1 and overall survival (OS). Here the prespecified final progression-free survival and interim OS analysis is reported. Patients randomly received benmelstobart and anlotinib plus etoposide/carboplatin (EC; n = 246), placebo and anlotinib plus EC (n = 245) or double placebo plus EC ('EC alone'; n = 247), followed by matching maintenance therapy. Compared with EC alone, median OS was prolonged with benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC (19.3 versus 11.9 months; hazard ratio 0.61; P = 0.0002), while improvement of OS was not statistically significant with anlotinib plus EC (13.3 versus 11.9 months; hazard ratio 0.86; P = 0.1723). The incidence of grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events was 93.1%, 94.3% and 87.0% in the benmelstobart and anlotinib plus EC, anlotinib plus EC, and EC alone groups, respectively. This study of immunochemotherapy plus multi-target anti-angiogenesis as first-line treatment achieved a median OS greater than recorded in prior randomized studies in patients with ES-SCLC. The safety profile was assessed as tolerable and manageable. Our findings suggest that the addition of anti-angiogenesis therapy to immunochemotherapy may represent an efficacious and safe approach to the management of ES-SCLC. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04234607 .
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that none of the authors has competing financial or nonfinancial interests as defined by Nature Portfolio.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

