ActivinA modulates B-acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cell communication and survival by inducing extracellular vesicles production
- PMID: 38992199
- PMCID: PMC11239915
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66779-3
ActivinA modulates B-acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cell communication and survival by inducing extracellular vesicles production
Abstract
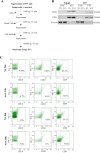
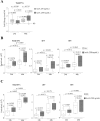
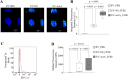
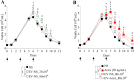
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are a new mechanism of cellular communication, by delivering their cargo into target cells to modulate molecular pathways. EV-mediated crosstalk contributes to tumor survival and resistance to cellular stress. However, the role of EVs in B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (B-ALL) awaits to be thoroughly investigated. We recently published that ActivinA increases intracellular calcium levels and promotes actin polymerization in B-ALL cells. These biological processes guide cytoskeleton reorganization, which is a crucial event for EV secretion and internalization. Hence, we investigated the role of EVs in the context of B-ALL and the impact of ActivinA on this phenomenon. We demonstrated that leukemic cells release a higher number of EVs in response to ActivinA treatment, and they can actively uptake EVs released by other B-ALL cells. Under culture-induced stress conditions, EVs coculture promoted cell survival in B-ALL cells in a dose-dependent manner. Direct stimulation of B-ALL cells with ActivinA or with EVs isolated from ActivinA-stimulated cells was even more effective in preventing cell death. This effect can be possibly ascribed to the increase of vesiculation and modifications of EV-associated microRNAs induced by ActivinA. These data demonstrate that ActivinA boosts EV-mediated B-ALL crosstalk, improving leukemia survival in stress conditions.
Keywords: ActivinA; B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia; Cell survival; Extracellular vesicles; Intercellular communication; Microenvironment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bashir M, Damineni S, Mukherjee G, Kondaiah P. Activin-A signaling promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition, invasion, and metastatic growth of breast cancer. npj Breast Cancer. 2015;1:1–13. doi: 10.1038/npjbcancer.2015.7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

