Comparative biological activity of palbociclib and ribociclib in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer
- PMID: 38992220
- PMCID: PMC11239654
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-67126-2
Comparative biological activity of palbociclib and ribociclib in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer
Abstract
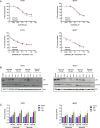
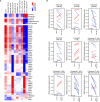
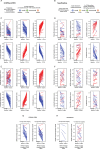
This study examines the biological effects of palbociclib and ribociclib in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, pivotal to the HARMONIA prospective phase III clinical trial. We explore the downstream impacts of these CDK4/6 inhibitors, focusing on cell lines and patient-derived tumor samples. We treated HR+ breast cancer cell lines (T47D, MCF7, and BT474) with palbociclib or ribociclib (100 nM or 500 nM), alone or combined with fulvestrant (1 nM), over periods of 24, 72, or 144 h. Our assessments included PAM50 gene expression, RB1 phosphorylation, Lamin-B1 protein levels, and senescence-associated β-galactosidase activity. We further analyzed PAM50 gene signatures from the CORALLEEN and NeoPalAna phase II trials. Both CDK4/6 inhibitors similarly inhibited proliferation across the cell lines. At 100 nM, both drugs partially reduced p-RB1, with further decreases at 500 nM over 144 h. Treatment led to reduced Lamin-B1 expression and increased senescence-associated β-galactosidase activity. Both drugs enhanced Luminal A and reduced Luminal B and proliferation signatures at both doses. However, the HER2-enriched signature significantly diminished only at the higher dose of 500 nM. Corresponding changes were observed in tumor samples from the CORALLEEN and NeoPalAna studies. At 2 weeks of treatment, both drugs significantly reduced the HER2-enriched signature, but at surgery, this reduction was consistent only with ribociclib. Our findings suggest that while both CDK4/6 inhibitors effectively modulate key biological pathways in HR+/HER2- breast cancer, nuances in their impact, particularly on the HER2-enriched signature, are dose-dependent, influenced by the addition of fulvestrant and warrant further investigation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.P. reports advisory and consulting fees from Roche, Pfizer, Novartis, Amgen, BMS, Puma, Oncolytics Biotech, MSD, Guardan Health, Peptomyc and Lilly, lecture fees from Roche, Pfizer, Novartis, Amgen, BMS, Nanostring Technologies and Daiichi Sankyo, institutional financial interests from Boehringer, Novartis, Roche, Nanostring, Sysmex Europa GmbH, Medica Scientia inno. Research, SL, Celgene, Astellas and Pfizer; stockholder and consultant of Reveal Genomics, SL; patents filed PCT/EP2016/080056, PCT/EP2022/086493, PCT/EP2023/060810, EP23382703 and EP23383369. F.B-M. has patents filed: PCT/EP2022/086493, PCT/EP2023/060810, EP23382703 and EP23383369 and part-time employment with Reveal Genomics, SL. J.G. reports scientific advisory board fees from Novartis, Pfizer and Lilly, consultancy training fees from Roche, Novartis and MSD, honoraria fees from Roche, Novartis and Pfizer. I.G-F. reports financing of courses and talks from Novartis. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cristofanilli, M. et al. Fulvestrant plus palbociclib versus fulvestrant plus placebo for treatment of hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer that progressed on previous endocrine therapy (PALOMA-3): Final analysis of the multicentre, double-blind, phas. Lancet Oncol.17(4), 425–439 (2016). 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00613-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

