Conditional PROTAC: Recent Strategies for Modulating Targeted Protein Degradation
- PMID: 38993102
- PMCID: PMC11581424
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202400326
Conditional PROTAC: Recent Strategies for Modulating Targeted Protein Degradation
Abstract
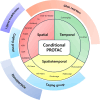
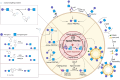
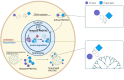
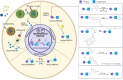
Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) have emerged as a promising technology for inducing targeted protein degradation by leveraging the intrinsic ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). While the potential druggability of PROTACs toward undruggable proteins has accelerated their rapid development and the wide-range of applications across diverse disease contexts, off-tissue effects and side-effects of PROTACs have recently received attentions to improve their efficacy. To address these issues, spatial or temporal target protein degradation by PROTACs has been spotlighted. In this review, we explore chemical strategies for modulating protein degradation in a cell type-specific (spatio-) and time-specific (temporal-) manner, thereby offering insights for expanding PROTAC applications to overcome the current limitations of target protein degradation strategy.
Keywords: PROTAC; Spatial PROTAC; Spatiotemporal PROTAC; Targeted Protein Degradation (TPD); Temporal PROTAC.
© 2024 The Author(s). ChemMedChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bett J. S., Essays Biochem. 2016, 60(2), 143–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RS-2023-00250887/National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning
- 2023R1A2C1007899/National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning
- 2021R1C1C1005766/National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning
- 2022R1C1C2008563/National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning
- RS-2023-00271205/National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

