Comparison of Robotic vs Open Cystectomy: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38993188
- PMCID: PMC11181804
- DOI: 10.3233/BLC-220065
Comparison of Robotic vs Open Cystectomy: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: The benefits of a robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) compared to an open approach is still under debate. Initial data on RARC were from trials where urinary diversion was performed by an extracorporeal approach, which does not represent a completely minimally invasive procedure. There are now updated data for RARC with intracorporeal urinary diversion that add to the evidence profile of RARC.
Objective: To perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness of RARC compared with open radical cystectomy (ORC).
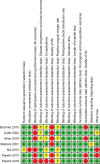
Materials and methods: Multiple databases were searched up to May 2022. We included randomised trials in which patients underwent RARC and ORC. Oncological and safety outcomes were assessed.
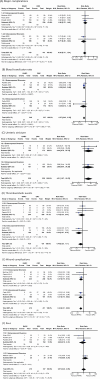
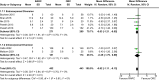
Results: Seven trials of 907 participants were included. There were no differences seen in primary outcomes: disease progression [RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.23], major complications [RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.72 to 1.24] and quality of life [SMD 0.05, 95% CI -0.13 to 0.38]. RARC resulted in a decreased risk of perioperative blood transfusion [RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.43 to 0.76], wound complications [RR 0.34, 95% CI 0.21 to 0.55] and reduced length of hospital stay [MD -0.62 days, 95% CI -1.11 to -0.13]. However, there was an increased risk of developing a ureteric stricture [RR 4.21, 95% CI 1.07 to 16.53] in the RARC group and a prolonged operative time [MD 70.4 minutes, 95% CI 34.1 to 106.7]. The approach for urinary diversion did not impact outcomes.
Conclusion: RARC is an oncologically safe procedure compared to ORC and provides the benefits of a minimally invasive approach. There was an increased risk of developing a ureteric stricture in patients undergoing RARC that warrants further investigation. There was no difference in oncological outcomes between approaches.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; complications; cystectomy; quality of life; robotic surgical procedures.
© 2023 – The authors. Published by IOS Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Konety and Lawrentschuk are Editorial Board members of this journal, but were not involved in the peer-review process nor had access to any information regarding its peer-review. Sathianathen, Pan, Furrer, Thomas, Dundee, Corcoran, Weight and Nair have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
References
-
- Tamhankar AS, Thurtle D, Hampson A, El-Taji O, Thurairaja R, Kelly JD, et al. Radical Cystectomy in England from 2013 to 2019 on 12,644 patients: An analysis of national trends and comparison of surgical approaches using Hospital Episode Statistics data. BJUI Compass. 2021;2(5):338–47. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matulewicz RS, DeLancey JO, Manjunath A, Tse J, Kundu SD, Meeks JJ. National comparison of oncologic quality indicators between open and robotic-assisted radical cystectomy. Urol Oncol. 2016;34(10):431.e9–e15. - PubMed
-
- Tan WS, Tan MY, Lamb BW, Sridhar A, Mohammed A, Baker H, et al. Intracorporeal robot-assisted radical cystectomy, together with an enhanced recovery programme, improves postoperative outcomes by aggregating marginal gains. BJU Int. 2018;121(4):632–9. - PubMed
-
- Satkunasivam R, Tallman CT, Taylor JM, Miles BJ, Klaassen Z, Wallis CJD. Robot-assisted Radical Cystectomy Versus Open Radical Cystectomy: A Meta-analysis of Oncologic, Perioperative, and Complication-related outcomes. Eur Urol Oncol. 2019;2(4):443–7. - PubMed
-
- Catto JWF, Khetrapal P, Ricciardi F, Ambler G, Williams NR, Al-Hammouri T, et al. Effect of Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy With Intracorporeal Urinary Diversion vs Open Radical Cystectomy on 90-Day Morbidity and Mortality Among Patients With Bladder Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama. 2022. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources