Potential therapeutic effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors on corneal diseases
- PMID: 38993197
- PMCID: PMC11238193
- DOI: 10.3389/ebm.2024.10142
Potential therapeutic effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors on corneal diseases
Abstract
The cornea is an avascular tissue in the eye that has multiple functions in the eye to maintain clear vision which can significantly impair one's vision when subjected to damage. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), a family of nuclear receptor proteins comprising three different peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) isoforms, namely, PPAR alpha (α), PPAR gamma (γ), and PPAR delta (δ), have emerged as potential therapeutic targets for treating corneal diseases. In this review, we summarised the current literature on the therapeutic effects of PPAR agents on corneal diseases. We discussed the role of PPARs in the modulation of corneal wound healing, suppression of corneal inflammation, neovascularisation, fibrosis, stimulation of corneal nerve regeneration, and amelioration of dry eye by inhibiting oxidative stress within the cornea. We also discussed the underlying mechanisms of these therapeutic effects. Future clinical trials are warranted to further attest to the clinical therapeutic efficacy.
Keywords: cornea; fibrosis; inflammation; neovascularisation; nerve regeneration; proliferator-activated receptors; wound healing.
Copyright © 2024 Chow, Lee, Liu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
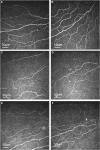
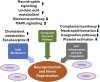
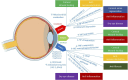
Similar articles
-
The role of PPAR in fungal keratitis.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 23;15:1454463. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1454463. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39763659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and PPAR agonists: the 'future' in dermatology therapeutics?Arch Dermatol Res. 2015 Nov;307(9):767-80. doi: 10.1007/s00403-015-1571-1. Epub 2015 May 19. Arch Dermatol Res. 2015. PMID: 25986745 Review.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor targets for the treatment of metabolic diseases.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:549627. doi: 10.1155/2013/549627. Epub 2013 May 27. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23781121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in healthy and diseased eyes.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Jul;208:108617. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108617. Epub 2021 May 16. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 34010603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking new avenues for neuropsychiatric disease therapy: the emerging potential of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors as promising therapeutic targets.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 Aug;241(8):1491-1516. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06617-6. Epub 2024 May 27. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38801530 Review.
Cited by
-
Pleiotropic Effects of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha and Gamma Agonists on Myocardial Damage: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Evidence-A Narrative Review.Cells. 2024 Sep 5;13(17):1488. doi: 10.3390/cells13171488. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39273057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Application of Terahertz Technology in Corneas and Corneal Diseases: A Systematic Review.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jan 8;12(1):45. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12010045. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39851319 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organisation. World report on vision –Executive summary (2024). Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/documents/publications/world-rep... (Accessed April 16, 2024).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

