CDKL3 is a promising biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis prediction in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38993199
- PMCID: PMC11237920
- DOI: 10.3389/ebm.2024.10106
CDKL3 is a promising biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis prediction in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
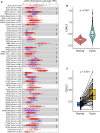
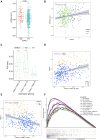
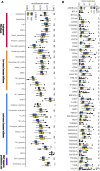
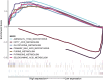
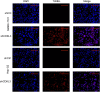
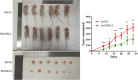
Cyclin-dependent kinase-like 3 (CDKL3) has been identified as an oncogene in certain types of tumors. Nonetheless, its function in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is poorly understood. In this study, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of CDKL3 based on data from the HCC cohort of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Our analysis included gene expression, diagnosis, prognosis, functional enrichment, tumor microenvironment and metabolic characteristics, tumor burden, mRNA expression-based stemness, alternative splicing, and prediction of therapy response. Additionally, we performed a cell counting kit-8 assay, TdT-mediated dUTP nick-end Labeling staining, migration assay, wound healing assay, colony formation assay, and nude mouse experiments to confirm the functional relevance of CDKL3 in HCC. Our findings showed that CDKL3 was significantly upregulated in HCC patients compared to controls. Various bioinformatic analyses suggested that CDKL3 could serve as a potential marker for HCC diagnosis and prognosis. Furthermore, CDKL3 was found to be involved in various mechanisms linked to the development of HCC, including copy number variation, tumor burden, genomic heterogeneity, cancer stemness, and alternative splicing of CDKL3. Notably, CDKL3 was also closely correlated with tumor immune cell infiltration and the expression of immune checkpoint markers. Additionally, CDKL3 was shown to independently function as a risk predictor for overall survival in HCC patients by multivariate Cox regression analysis. Furthermore, the knockdown of CDKL3 significantly inhibited cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo, indicating its role as an oncogene in HCC. Taken together, our findings suggest that CDKL3 shows promise as a biomarker for the detection and treatment outcome prediction of HCC patients.
Keywords: CDKL3; biomarker; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognosis; the cancer genome atlas.
Copyright © 2024 Wu, Lu, Ouyang, Zhou, Lei, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Midmer M, Haq R, Squire JA, Zanke BW. Identification of NKIAMRE, the human homologue to the mitogen-activated protein kinase-/cyclin-dependent kinase-related protein kinase NKIATRE, and its loss in leukemic blasts with chromosome arm 5q deletion. Cancer Res (1999) 59:4069–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

