Significance and Possible Biological Mechanism for CLDN8 Downregulation in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma Tissues
- PMID: 38993257
- PMCID: PMC11236366
- DOI: 10.14740/wjon1869
Significance and Possible Biological Mechanism for CLDN8 Downregulation in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma Tissues
Abstract
Background: The clinical role of claudin 8 (CLDN8) in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC) remains unclarified. Herein, the expression level and potential molecular mechanisms of CLDN8 underlying KIRC were determined.
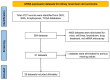
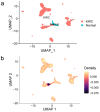
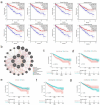
Methods: High-throughput datasets of KIRC were collected from GEO, ArrayExpress, SRA, and TCGA databases to determine the mRNA expression level of the CLDN8. In-house tissue microarrays and immunochemistry were performed to examine CLDN8 protein expression. A summary receiver operating characteristic curve (SROC) and standardized mean difference (SMD) forest plot were generated using Stata v16.0. Single-cell analysis was conducted to further prove the expression level of CLDN8. A clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats knockout screen analysis was executed to assess the growth impact of CLDN8. Functional enrichment analysis was conducted using the Metascape database. Additionally, single-sample gene set enrichment analysis was implied to explore immune cell infiltration in KIRC.
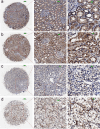
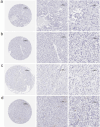
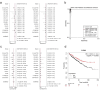
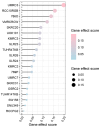
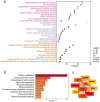
Results: A total of 17 mRNA datasets comprising 1,060 KIRC samples and 452 non-cancerous control samples were included in this study. Additionally, 105 KIRC and 16 non-KIRC tissues were analyzed using in-house immunohistochemistry. The combined SMD was -5.25 (95% confidence interval (CI): -6.13 to -4.37), and CLDN8 downregulation yielded an SROC area under the curve (AUC) close to 1.00 (95% CI: 0.99 - 1.00). CLDN8 downregulation was also confirmed at the single-cell level. Knocking out CLDN8 stimulated KIRC cell proliferation. Lower CLDN8 expression was correlated with worse overall survival of KIRC patients (hazard ratio of CLDN8 downregulation = 1.69, 95% CI: 1.2 - 2.4). Functional pathways associated with CLDN8 co-expressed genes were centered on carbon metabolism obstruction, with key hub genes ACADM, ACO2, NDUFS1, PDHB, SDHD, SUCLA2, SUCLG1, and SUCLG2.
Conclusions: CLDN8 is downregulated in KIRC and is considered a potential tumor suppressor. CLDN8 deficiency may promote the initiation and progression of KIRC, potentially in conjunction with metabolic dysfunction.
Keywords: CLDN8; Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; Mechanism; Prognosis; Tissue microarray.
Copyright 2024, Ji et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low expression of fatty acid oxidation related gene ACADM indicates poor prognosis of renal clear cell carcinoma and is related to tumor immune infiltration.Oncol Res. 2024 Feb 6;32(3):545-561. doi: 10.32604/or.2023.030462. eCollection 2024. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 38361759 Free PMC article.
-
Low expression of SLC34A1 is associated with poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.BMC Urol. 2023 Mar 28;23(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12894-023-01212-x. BMC Urol. 2023. PMID: 36978048 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive analysis of essential meiotic endonuclease 1 to prognosis and immune infiltration in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024 Jan;28(2):584-602. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202401_35056. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38305603
-
Supervised Learning and Multi-Omics Integration Reveals Clinical Significance of Inner Membrane Mitochondrial Protein (IMMT) in Prognostic Prediction, Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Precision Medicine for Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 15;24(10):8807. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108807. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240154 Free PMC article.
-
GRAMD1A Is a Biomarker of Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma and Is Associated with Immune Infiltration in the Tumour Microenvironment.Dis Markers. 2022 Jul 11;2022:5939021. doi: 10.1155/2022/5939021. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35860689 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Expression and Targeted Application of Claudins Family in Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Sep 25;11:1801-1821. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S483861. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 39345937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
