Hemisection: A Paradigm Shift in Prolonging Tooth Viability
- PMID: 38993416
- PMCID: PMC11238756
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.62127
Hemisection: A Paradigm Shift in Prolonging Tooth Viability
Abstract
Splitting a molar means removing or separating the root and the accompanying crown portion. Hemisection of a damaged tooth aids in preserving the tooth structure and the existing alveolar bone surrounding the preserved root while also enabling the installation of a fixed prosthesis. This case report defines hemisection as an effective modality for preserving carious mandibular first molars with periodontal and periapical pathology.
Keywords: cbct; dental canal; hemisection; mandibular molar; root resection.
Copyright © 2024, Manik et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve human participants or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
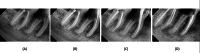
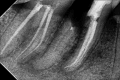
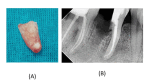
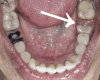
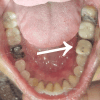

Similar articles
-
Hemisection as a Conservative Management of Grossly Carious Permanent Mandibular First Molar.J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2018 Jan-Jun;9(1):97-99. doi: 10.4103/jnsbm.JNSBM_53_17. J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 29456402 Free PMC article.
-
Conservative management of grossly carious mandibular first molar with a hemisection approach: a case report.Gen Dent. 2015 Jul-Aug;63(4):19-21. Gen Dent. 2015. PMID: 26147162
-
Combined implant-residual tooth supported prosthesis after tooth hemisection: A finite element analysis.Ann Anat. 2016 Jul;206:96-103. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2016.01.002. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Ann Anat. 2016. PMID: 26851558 Clinical Trial.
-
Hemisection and root amputation.J Am Dent Assoc. 1986 Apr;112(4):511-8. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1986.0050. J Am Dent Assoc. 1986. PMID: 3517109 Review.
-
Evaluation of root canal morphology of human primary molars by using CBCT and comprehensive review of the literature.Acta Odontol Scand. 2016;74(4):250-8. doi: 10.3109/00016357.2015.1104721. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Acta Odontol Scand. 2016. PMID: 26523502 Review.
References
-
- The pulpal pocket approach: retrograde periodontitis. Simring M, Goldberg M. J Periodontol. 1964;35:22–48.
-
- An innovative approach for treating vertically fractured mandibular molar - hemisection with socket preservation. Agrawal VS, Kapoor S, Shah NC. J Interdiscip Dent. 2012;2:141–143.
-
- Carvalho S, Moreira C, Oliveira A, et al. Nanobiomaterials in Clinical Dentistry. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier B.V.; 2019. Bioactive glass nanoparticles for periodontal regeneration and applications in dentistry; pp. 351–383.
-
- The role of resective periodontal surgery in the treatment of furcation defects. DeSanctis M, Murphy KG. Periodontol 2000. 2000;22:154–168. - PubMed
-
- Management of periodontally compromised mandibular molar with hemisectioning: a case report. Napte B, Raghavendra SS. J Int Clin Dent Res Organ. 2014;6:130–133.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
