Investigation and Management of Lower Limb Septic Arthritis in Children: An Update Using the Latest British Orthopaedic Association Standard for Trauma (BOAST) Guidelines
- PMID: 38993437
- PMCID: PMC11238896
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.62179
Investigation and Management of Lower Limb Septic Arthritis in Children: An Update Using the Latest British Orthopaedic Association Standard for Trauma (BOAST) Guidelines
Abstract
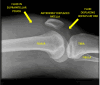
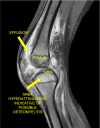
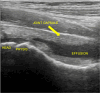
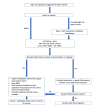
Septic arthritis is a serious condition in children, with the hip and knee joints most typically affected. Patients typically present with pain, joint swelling, fever, and an inability to bear weight. Early recognition and treatment are crucial, as untreated septic arthritis can lead to serious complications, including sepsis, irreversible joint damage, growth problems, and early-onset arthritis. Clinical signs, inflammatory markers, and imaging are used for the diagnosis of septic arthritis. The mainstay of management includes antibiotic therapy and surgical washout. Long-term follow-up is essential to monitor for complications.
Keywords: child; joint infection; knee and hip; lower limb; pediatric orthopedics; sepsis; septic arthritis.
Copyright © 2024, Sebastiao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Intellectual property info: Images used in the article are referenced and cited from radiopaedia.org. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Krogstad P. Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2004. Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis; pp. 713–736.
-
- The management of septic arthritis in children: systematic review of the English language literature. Kang SN, Sanghera T, Mangwani J, Paterson JM, Ramachandran M. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91:1127–1133. - PubMed
-
- Septic arthritis in children. Wall C, Donnan L. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25901405/ Aust Fam Physician. 2015;44:213–215. - PubMed
-
- Sequelae of pediatric osteoarticular infection. Ilharreborde B. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101:0–37. - PubMed
-
- Long-term outcomes of acute osteoarticular infections in children. Manz N, Krieg AH, Buettcher M, Ritz N, Heininger U. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2020.587740. Front Pediatr. 2020;8:587740. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
