Proteomic and metabolomic profiling of methicillin resistant versus methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus using a simultaneous extraction protocol
- PMID: 38993491
- PMCID: PMC11238212
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1402796
Proteomic and metabolomic profiling of methicillin resistant versus methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus using a simultaneous extraction protocol
Abstract
Background: Understanding the biology of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is crucial to unlocking insights for new targets in our fight against this antimicrobial resistant priority pathogen. Although proteomics and metabolomic profiling offer the potential to elucidating such biological markers, reports of methodological approaches for carrying this out in S. aureus isolates remain limited. We describe the use of a dual-functionality methanol extraction method for the concurrent extraction of protein and metabolites from S. aureus and report on the comparative analysis of the proteomic and metabolomic profiles of MRSA versus methicillin sensitive S. aureus (MSSA).
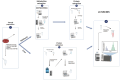
Methods: Bacterial reference strains MRSA ATCC43300 and MSSA ATCC25923 were used. The conventional urea methodology was used for protein extraction and a methanol based method was used for concurrent proteins and metabolites extraction. Proteomic and metabolomic profiling was carried out using TimsTOF mass spectrometry. Data processing was carried out using the MaxQuant version 2.1.4.0.
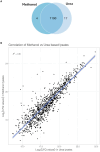
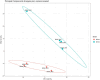
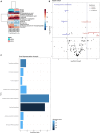
Results: This study represents the first report on the utilization of the methanol extraction method for concurrent protein and metabolite extraction in Gram positive bacteria. Our findings demonstrate good performance of the method for the dual extraction of proteins and metabolites from S. aureus with demonstration of reproducibility. Comparison of MRSA and MSSA strains revealed 407 proteins with significantly different expression levels. Enrichment analysis of those proteins revealed distinct pathways involved in fatty acid degradation, metabolism and beta-lactam resistance. Penicillin-binding protein PBP2a, the key determinant of MRSA resistance, exhibited distinct expression patterns in MRSA isolates. Metabolomic analysis identified 146 metabolites with only one exclusive to the MRSA. The enriched pathways identified were related to arginine metabolism and biosynthesis.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate the effectiveness of the methanol-based dual-extraction method, providing simultaneous insights into the proteomic and metabolomic landscapes of S. aureus strains. These findings demonstrate the utility of proteomic and metabolomic profiling for elucidating the biological basis of antimicrobial resistance.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; gram positive bacteria; mass spectrometry; metabolomics; proteomics.
Copyright © 2024 Boucherabine, Giddey, Nassar, Al-Hroub, Mohamed, Harb, Soares and Senok.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nontargeted metabolomics reveals differences in the metabolite profiling among methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in response to antibiotics.Mol Omics. 2022 Dec 5;18(10):948-956. doi: 10.1039/d2mo00229a. Mol Omics. 2022. PMID: 36218091
-
Molecular-Characterization of Methicillin-Resistance Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from Different Tertiary Care Hospitals in Bangladesh.Mymensingh Med J. 2017 Jan;26(1):37-44. Mymensingh Med J. 2017. PMID: 28260753
-
Comparative Proteomic Profiling of Methicillin-Susceptible and Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Proteomics. 2020 Jan;20(2):e1900221. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201900221. Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31872541
-
A Review on Five and Six-Membered Heterocyclic Compounds Targeting the Penicillin-Binding Protein 2 (PBP2A) of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).Molecules. 2023 Oct 10;28(20):7008. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207008. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37894491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation Between Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in MRSA and MSSA Isolated from Clinical Samples in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Microb Drug Resist. 2020 Sep;26(9):1071-1080. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0001. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Microb Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32159447
Cited by
-
Proteomic Insights into Bacterial Responses to Antibiotics: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 27;26(15):7255. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157255. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MALDI-TOF MS Biomarkers for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Detection: A Systematic Review.Metabolites. 2025 Aug 8;15(8):540. doi: 10.3390/metabo15080540. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40863157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Atshan S. S., Shamsudin M. N., Sekawi Z., Thian Lung L. T., Barantalab F., Liew Y. K., et al. . (2015). Comparative proteomic analysis of extracellular proteins expressed by various clonal types of Staphylococcus aureus and during planktonic growth and biofilm development. Front. Microbiol. 6:524. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00524 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

