Patient-reported outcomes for the phase 3 FURLONG study of furmonertinib versus gefitinib as first-line therapy for Chinese patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 38993541
- PMCID: PMC11238182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2024.101122
Patient-reported outcomes for the phase 3 FURLONG study of furmonertinib versus gefitinib as first-line therapy for Chinese patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Furmonertinib showed superior efficacy compared with gefitinib as first-line therapy in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in the FURLONG study. Here we present prespecified secondary endpoints of patient-reported outcomes (PRO).
Methods: In this multicentre, double-blind, double-dummy, randomised phase 3 study, patients were 1:1 randomly assigned to receive furmonertinib 80 mg once daily or gefitinib 250 mg once daily. PROs assessed by the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality-of-Life Questionnaire Core 30 and Quality-of-Life Questionnaire Lung Cancer 13 were analysed using a mixed model for repeated measures and time-to-event analyses. A difference in score of 10 points or more was deemed clinically relevant.
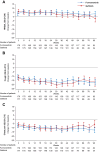
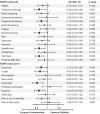
Findings: Three hundred and fifty-seven patients (furmonertinib group, n = 178; gefitinib group, n = 179) received at least one dose of the study drug, all of whom completed at least one PRO assessment. Statistically significant difference of overall score changes from baseline favoured furmonertinib in physical functioning (between-group difference 2.14 [95% CI 0.25-4.04], p = 0.027), nausea/vomiting (-1.56 [95% CI -2.62 to -0.49], p = 0.004), appetite loss (-2.24 [95% CI -4.26 to -0.23], p = 0.029), diarrhoea (-3.36 [95% CI -5.19 to -1.54], p < 0.001), alopecia (-2.62 [95% CI -4.54 to -0.71], p = 0.007), and pain in other parts (-4.55 [95% CI -7.37 to -1.74], p = 0.002), but not reached clinical relevance. Time to deterioration in physical functioning (hazard ratio 0.63 [95% CI 0.42-0.94], p = 0.021), cognitive functioning (0.73 [95% CI 0.54-0.98], p = 0.034), nausea/vomiting (0.64 [95% CI 0.41-0.99], p = 0.042), appetite loss (0.63 [95% CI 0.43-0.92], p = 0.016), diarrhoea (0.63 [95% CI 0.46-0.85], p = 0.002), dyspnoea (0.72 [95% CI 0.53-0.98], p = 0.034), cough (0.67 [95% CI 0.44-1.00], p = 0.049), dysphagia (0.54 [95% CI 0.35-0.83], p = 0.004), and alopecia (0.62 [95% CI 0.42-0.90], p = 0.012) was longer with furmonertinib versus gefitinib.
Interpretation: In patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC, furmonertinib showed improved scores and delayed deterioration in several functioning and symptoms compared to gefitinib.
Funding: Shanghai Allist Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd and the National Science and Technology Major Project for Key New Drug Development (2017ZX09304015).
Keywords: AST2818; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Furmonertinib; Non-small cell lung cancer; Patient-reported outcomes.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
JH, FL, YJ and NG are employees and shareholders of Shanghai Allist Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Mok T.S., Wu Y.-L., Thongprasert S., et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin–paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:947–957. - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T., Morita S., Yatabe Y., et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:121–128. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C., Wu Y.-L., Chen G., et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:735–742. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

