Effect of time-restricted eating regimen on weight loss is mediated by gut microbiome
- PMID: 38993674
- PMCID: PMC11238135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110202
Effect of time-restricted eating regimen on weight loss is mediated by gut microbiome
Abstract
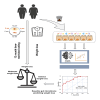
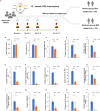
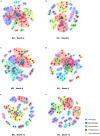
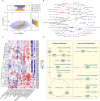
Time-restricted eating (TRE) is a promising obesity management strategy, but weight-loss efficacy varies among participants, and the underlying mechanism is unclear. The study aimed to investigate the role of gut microbiota in weight-loss response during long-term TRE intervention. We analyzed data from 51 obese adults in a 12-month TRE program, categorizing them into distinct weight loss groups (DG) and moderate weight loss groups (MG) based on their TRE responses. Shotgun metagenomic sequencing analysis revealed a significant increase in species closely associated with weight loss effectiveness and metabolic parameter changes in the DG group. Pathways related to fatty acid biosynthesis, glycogen biosynthesis, and nucleotide metabolism were reduced in the DG group and enhanced in the MG group. Next, we identified nine specific species at baseline that contributed better responses to TRE intervention and significant weight loss. Collectively, gut microbiota contributes to responsiveness heterogeneity in TRE and can predict weight-loss effectiveness.
Keywords: Human metabolism; Microbial genomics; Microbiome; Physiology.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Jensen M.D., Ryan D.H., Apovian C.M., Ard J.D., Comuzzie A.G., Donato K.A., Hu F.B., Hubbard V.S., Jakicic J.M., Kushner R.F., et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014;63:2985–3023. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.004. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

