Control of a chemical chaperone by a universally conserved ATPase
- PMID: 38993675
- PMCID: PMC11237923
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110215
Control of a chemical chaperone by a universally conserved ATPase
Abstract
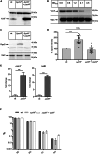
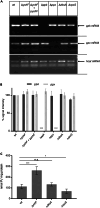
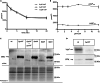
The universally conserved YchF/Ola1 ATPases regulate stress response pathways in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Deletion of YchF/Ola1 leads to increased resistance against environmental stressors, such as reactive oxygen species, while their upregulation is associated with tumorigenesis in humans. The current study shows that in E. coli, the absence of YchF stimulates the synthesis of the alternative sigma factor RpoS by a transcription-independent mechanism. Elevated levels of RpoS then enhance the transcription of major stress-responsive genes. In addition, the deletion of ychF increases the levels of polyphosphate kinase, which in turn boosts the production of the evolutionary conserved and ancient chemical chaperone polyphosphate. This potentially provides a unifying concept for the increased stress resistance in bacteria and eukaryotes upon YchF/Ola1 deletion. Intriguingly, the simultaneous deletion of ychF and the polyphosphate-degrading enzyme exopolyphosphatase causes synthetic lethality in E. coli, demonstrating that polyphosphate production needs to be fine-tuned to prevent toxicity.
Keywords: Applied sciences; Biotechnology; Medical biochemistry.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Role of the Universally Conserved ATPase YchF/Ola1 in Translation Regulation during Cellular Stress.Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 23;10(1):14. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10010014. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 35056463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox Activation of the Universally Conserved ATPase YchF by Thioredoxin 1.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Jan 20;24(3):141-56. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6272. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 26160547 Free PMC article.
-
The Universally Conserved ATPase YchF Regulates Translation of Leaderless mRNA in Response to Stress Conditions.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 7;8:643696. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.643696. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34026826 Free PMC article.
-
A universally conserved ATPase regulates the oxidative stress response in Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 21;287(52):43585-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.413070. Epub 2012 Nov 8. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23139412 Free PMC article.
-
The Universally Conserved Unconventional G Protein YchF Is Critical for Growth and Stress Response.Life (Basel). 2023 Apr 20;13(4):1058. doi: 10.3390/life13041058. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37109587 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Silver-Ruthenium-Based Antimicrobial Kills Gram-Negative Bacteria Through Oxidative Stress-Induced Macromolecular Damage.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 4:2025.01.03.631245. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.03.631245. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: mSphere. 2025 Jun 25;10(6):e0001725. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00017-25. PMID: 39803548 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A novel silver-ruthenium-based antimicrobial kills Gram-negative bacteria through oxidative stress-induced macromolecular damage.mSphere. 2025 Jun 25;10(6):e0001725. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00017-25. Epub 2025 May 30. mSphere. 2025. PMID: 40444966 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

