Rituximab versus tacrolimus as corticosteroid-sparing therapy for children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and nonrandomized controlled trials
- PMID: 38993828
- PMCID: PMC11236076
- DOI: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_234_23
Rituximab versus tacrolimus as corticosteroid-sparing therapy for children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and nonrandomized controlled trials
Abstract
Objectives: Prolonged use of corticosteroids induced complicated course in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome (SDNS), and the use of tacrolimus, a first-line alternative calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) agent was related to some unwanted adverse effects. Rituximab, a second alternative treatment has been proven to reliably reduce the number of relapses within 12 months with minimal adverse effects.
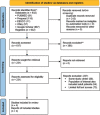
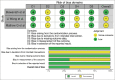
Materials and methods: Our review follows Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis guidelines. All the databases were derived from MEDLINE, Proquest, EBSCOhost, Wiley, and Google Scholar within the past 11 years. The risk of bias was evaluated using the Revised Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool for Randomized Trials (RoB 2) and Risk of Bias in Non-Randomized Studies of Interventions. Meta-analysis used Review Manager (version 5.4) with a random effect model to obtain a pooled mean difference (MD) and odds ratio with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
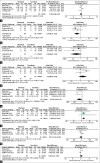
Results: Four studies were included based on our eligibility criteria, and only three were included in the quantitative analysis. Three studies had low and one study had a moderate risk of bias. Pooled data results indicated that Rituximab was superior to tacrolimus in reducing the number of patients with 1-2 relapses (MD = 0.44, [95% CI: 0.21-0.91]) and had higher eGFR values (MD = 6.67; [CI - 2.92-10.61]). However, Rituximab showed insignificant superiority compared to tacrolimus in reducing the number of patients with 3 relapses, sustained remission, cumulative steroid use, serum cholesterol, and serum albumin concentrations.
Conclusion: Rituximab exhibits more advantages in treating SDNS compared to tacrolimus, although the treatment options are highly individualized. Both regimens must also be weighed against their potential side effects to achieve a better overall health status.
Keywords: Children; Rituximab; Steroid-dependent Nephrotic syndrome; Tacrolimus.
Copyright: © 2024 Tzu Chi Medical Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
