Worldwide variations in COVID-19 vaccination policies and practices in liver transplant settings: results of a multi-society global survey
- PMID: 38993892
- PMCID: PMC11235330
- DOI: 10.3389/frtra.2023.1332616
Worldwide variations in COVID-19 vaccination policies and practices in liver transplant settings: results of a multi-society global survey
Abstract
Background: Despite the WHO's report of 24 available SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, limited data exist regarding vaccination policies for liver transplant (LT) patients. To address this, we conducted a global multi-society survey (EASL-ESOT-ELITA-ILTS) in LT centers.
Methods: A digital questionnaire assessing vaccine policies, safety, efficacy, and center data was administered online to LT centers.
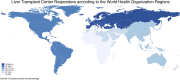
Results: Out of 168 responding centers, 46.4%, 28%, 13.1%, 10.7%, and 1.8% were from European, American, Western Pacific, Southeast Asian, and Eastern Mediterranean Regions. Most LT centers prioritized COVID-19 vaccine access for LT patients (76%) and healthcare workers (86%), while other categories had lower priority (30%). One-third of responders recommended mRNA vaccine exclusively, while booster doses were widely recommended (81%). One-third conducted post-vaccine liver function tests post COVID-19 vaccine. Only 16% of centers modified immunosuppression, and mycophenolate discontinuation or modification was the main approach. Side effects were seen in 1 in 1,000 vaccinated patients, with thromboembolism, acute rejection, and allergic reaction being the most severe. mRNA showed fewer side effects (-3.1, p = 0.002).
Conclusion: COVID-19 vaccines and booster doses were widely used among LT recipients and healthcare workers, without a specific vaccine preference. Preventative immunosuppression adjustment post-vaccination was uncommon. mRNA vaccines demonstrated a favorable safety profile in this population.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; liver; policy; side effect; survey; transplant; vaccine; worldwide activity.
© 2024 Di Maira, Vinaixa, Izzy, Paolo Russo, Kirchner, Rammohan, Belli, Polak, Berg and Berenguer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard > cases [dashboard]. (2023). Available at: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases (accessed September 20, 2022).
-
- Watson OJ, Barnsley G, Toor J, Hogan AB, Winskill P, Ghani AC. Global impact of the first year of COVID-19 vaccination: a mathematical modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis. (2022) 22(9):1293–1302. 10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00320-6. Erratum in: Lancet Infect Dis. (2023) 23(10):e400. PMID: 35753318; PMCID: PMC9225255 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

