Tregs in transplantation tolerance: role and therapeutic potential
- PMID: 38993904
- PMCID: PMC11235334
- DOI: 10.3389/frtra.2023.1217065
Tregs in transplantation tolerance: role and therapeutic potential
Abstract
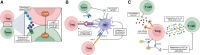
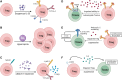
CD4+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) are indispensable for preventing autoimmunity, and they play a role in cancer and transplantation settings by restraining immune responses. In this review, we describe evidence for the importance of Tregs in the induction versus maintenance of transplantation tolerance, discussing insights into mechanisms of Treg control of the alloimmune response. Further, we address the therapeutic potential of Tregs as a clinical intervention after transplantation, highlighting engineered CAR-Tregs as well as expansion of donor and host Tregs.
Keywords: Foxp 3; Tregs (regulatory T cells); acute rejection (AR); alloimmunity; tolerance; transplantation.
© 2023 Cassano, Chong and Alegre.
Conflict of interest statement
The author M-LA declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. (1995) 155(3):1151–64. 10.4049/jimmunol.155.3.1151 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

