From biogenesis to aptasensors: advancements in analysis for tumor-derived extracellular vesicles research
- PMID: 38994022
- PMCID: PMC11234286
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.95885
From biogenesis to aptasensors: advancements in analysis for tumor-derived extracellular vesicles research
Abstract
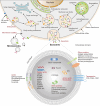
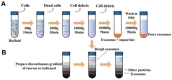
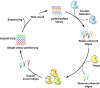
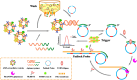
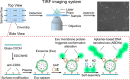
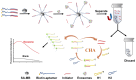
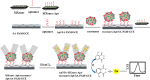
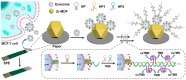
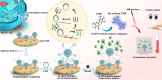
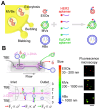
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are enclosed by a nanoscale phospholipid bilayer membrane and typically range in size from 30 to 200 nm. They contain a high concentration of specific proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids, reflecting but not identical to the composition of the parent cell. The inherent characteristics and variety of EVs give them extensive and unique advantages in the field of cancer identification and treatment. Recently, EVs have been recognized as potential tumor markers for the detection of cancer. Aptamers, which are molecules of single-stranded DNA or RNA, demonstrate remarkable specificity and affinity for their targets by adopting distinct tertiary structures. Aptamers offer various advantages over their protein counterparts, such as reduced immunogenicity, the ability for convenient large-scale synthesis, and straightforward chemical modification. In this review, we summarized EVs biogenesis, sample collection, isolation, storage and characterization, and finally provided a comprehensive survey of analysis techniques for EVs detection that are based on aptamers.
Keywords: Aptamers; Detection; Extracellular Vesicles; Tumor Markers.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An orthogonal barcoding enabled smart nanodevice for highly efficient isolation and proteomic profiling of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles.Analyst. 2025 Jun 9;150(12):2514-2523. doi: 10.1039/d5an00348b. Analyst. 2025. PMID: 40401310
-
The role of tissue-derived extracellular vesicles in tumor microenvironment.Tissue Cell. 2024 Aug;89:102470. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2024.102470. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Tissue Cell. 2024. PMID: 39002287 Review.
-
Isolation of extracellular vesicles with multivalent aptamers.Analyst. 2021 Jan 4;146(1):253-261. doi: 10.1039/d0an01420f. Analyst. 2021. PMID: 33107503
-
[Efficient capture and proteomics analysis of urinary extracellular vesicles by affinity purification].Se Pu. 2025 May;43(5):508-517. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2024.11013. Se Pu. 2025. PMID: 40331614 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Biosensing extracellular vesicles: contribution of biomolecules in affinity-based methods for detection and isolation.Analyst. 2020 Mar 21;145(6):1997-2013. doi: 10.1039/c9an01949a. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Analyst. 2020. PMID: 31960838 Review.
References
-
- Huang R, He L, Jin L, Li Z, He N, Miao W. Recent advancements in DNA nanotechnology-enabled extracellular vesicles detection and diagnosis: A mini review. Chin Chem Lett. 2023;34:107926.
-
- Wang T, Fu Y, Sun S, Huang C, Yi Y, Wang J. et al. Exosome-based drug delivery systems in cancer therapy. Chin Chem Lett. 2023;34:107508.
-
- Pegtel DM, Gould SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88:487–514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

